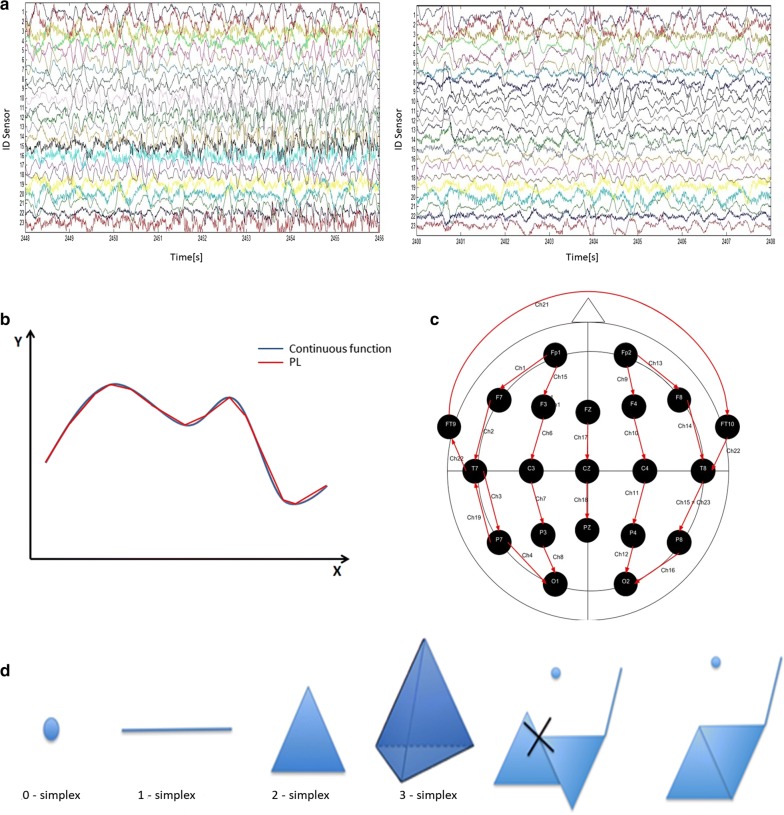
Fig. 1.
a Examples of epileptic (on the left) and healthy (on the right) EEG recordings. The amplitude of each signal is in V. b An example of a PL. c Graphical scheme representing the positions of the electrodes during an EEG. The arrows correspond to the 23 potential differences that are recorded. d Geometrical representation of some simplices, followed by an aggregation of simplices that is not a simplicial complex because the intersection of the two triangles is not a face of any of them. The last aggregation is a proper simplicial complex