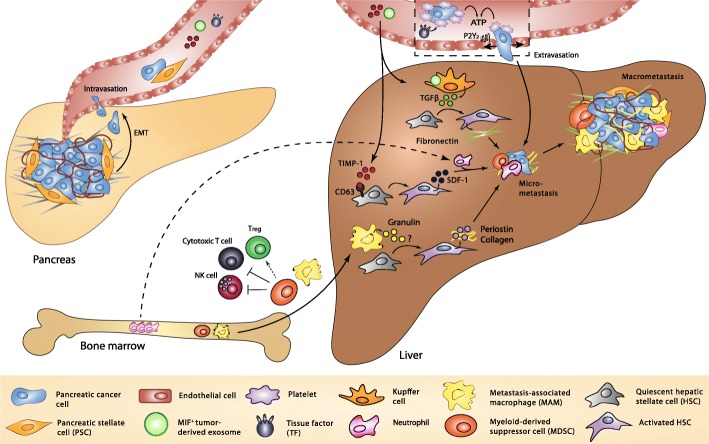
Fig. 1.
Molecular and cellular events involved in PMN formation in PDAC. PSCs and matrix stiffness, part of the tumor-associated stroma, assist invasion and intravasation of pancreatic cancer cells, for example by inducing EMT. Meanwhile in the hepatic microenvironment, platelet activation and thrombus formation in response to microparticle-associated TF secreted by the primary tumor facilitates the arrest of disseminated pancreatic cancer cells. Opening of the endothelial barrier by activated platelets then facilitates their extravasation. Exosomes enriched in MIF shed by pancreatic cancer cells interact with Kupffer cells, which activate HSCs via the release of TGFβ. The deposition of fibronectin by activated HSCs provides docking sites for metastasis-promoting bone marrow-derived cells such as macrophages and MDSCs. MDSCs impose immune tolerance by inhibiting NK cells and cytotoxic T cells and by promoting the development of Treg. Pancreatic cancer cell-derived TIMP-1 activates HSCs via its cognate receptor CD63 and induces the secretion of SDF-1, a chemoattractant for bone marrow-derived neutrophils. HSCs are also activated in response to MAM-derived granulin, which induces the production of periostin and collagen by HSCs. MAMs also inhibit anti-tumor immune responses by taking on an immunosuppressive M2 phenotype. PSC, pancreatic stellate cell; EMT, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition; TF, tissue factor; MIF, macrophage inhibitory factor; HSC, hepatic stellate cell; TGFβ, transforming growth factor β; MDSC, myeloid-derived suppressor cell; NK cell, natural killer cell; Treg, regulatory T cell; TIMP-1, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1; CD63, cluster of differentiation 63; SDF-1, stromal-derived factor-1; MAM, metastasis-associated macrophage