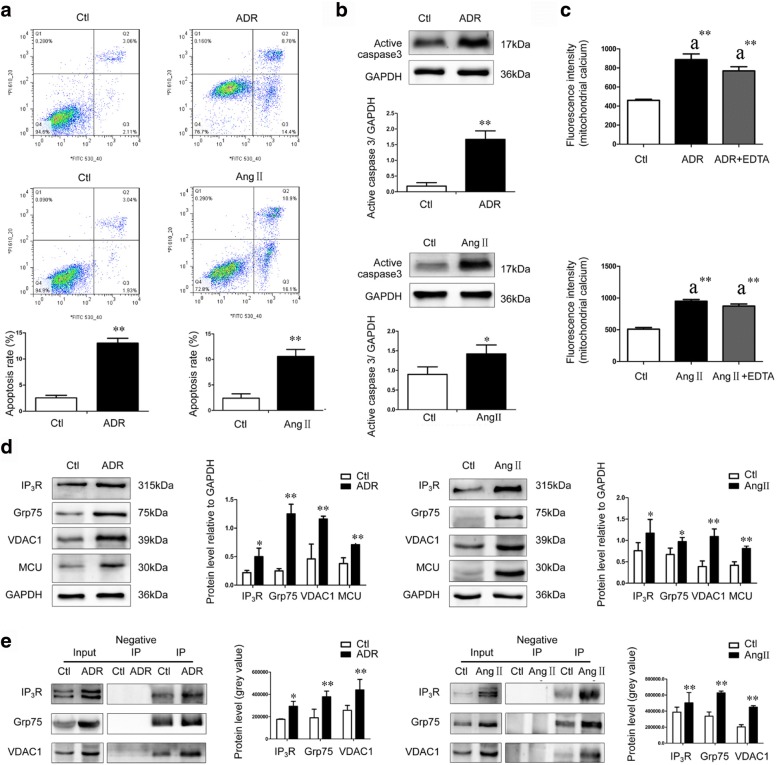
Fig. 1.
IP3R-Grp75-VDAC1-MCU axis, mitochondrial Ca2+, and apoptosis in podocytes treated with ADR and Ang II. Ctl, control; ADR, Adriamycin; Ang II, angiotensin II; IP3R, inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate receptor; Grp75, glucose-regulated protein 75; VDAC1, voltage dependent anion channel 1; MCU, mitochondrial calcium uniporter; a, compared with the Ctl group; **, P < 0.01; *, P < 0.05. Compared with the Ctl podocytes, a) The cells in Q3 which were annexin high and PI low were counted as apoptotic cells. Significantly increased apoptosis rate was found in ADR- (n = 3) and Ang II-treated podocytes (n = 3), b) Significantly increased levels of active caspase-3 was found in podocytes treated with ADR (n = 4) and Ang II (n = 4), c) Mitochondrial Ca2+ levels were increased in podocytes treated with ADR (n = 12) and Ang II (n = 12), d) Significantly increased expression of IP3R, Grp75, VDAC1, and MCU were found in podocytes treated with ADR (n = 6) and Ang II (n = 6). e Co-IP were performed to analyze the IP3R-Grp75-VDAC1 interaction. Normal rabbit IgG without antigenicity was used as a negative control. Lysates from both Ctl and ADR- or Ang-II treated podocytes without immunoprecipitation were used as a positive control (input). The proteins pulled down by anti-Grp75 antibodies was analyzed by western blotting. Compared with the Ctl podocytes, there was a significant increase in the amount of IP3R, Grp75, and VDAC1 in pulled down samples from ADR- (n = 3) or Ang II-treated podocytes (n = 3)