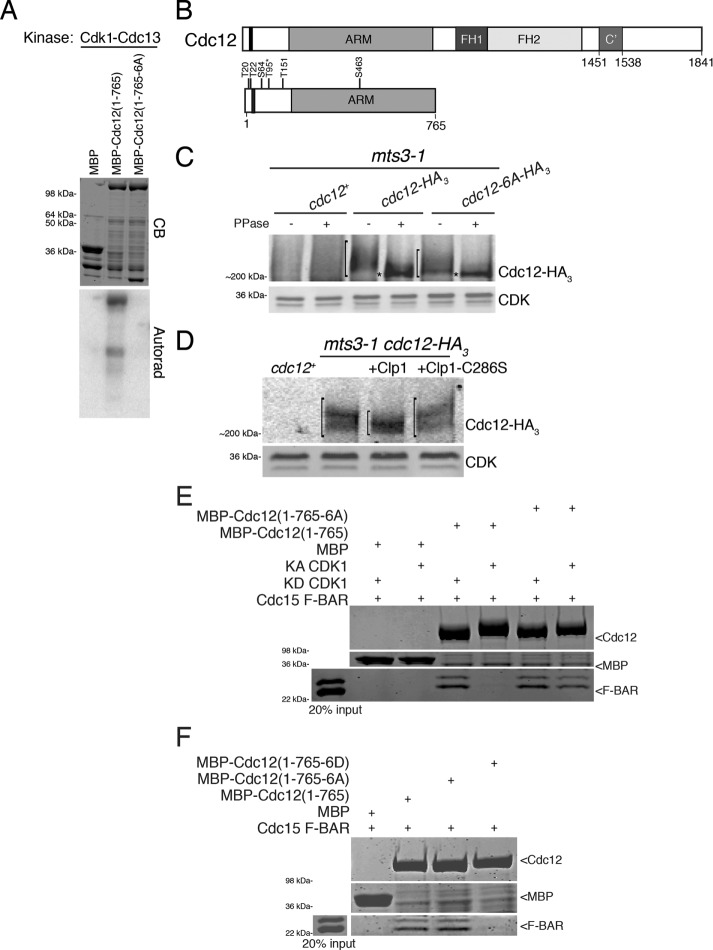
FIGURE 1:
Cdc12 is a Cdk1 substrate. (A) In vitro kinase assay using Cdk1–Cdc13 purified from insect cells and bacterially produced MBP, MBP-Cdc12(1–765), and MBP-Cdc12(1–765-6A) fragments. The gel was stained with Coomassie blue (CB) and proteins labeled by γ–P32 were detected by autoradiography. (B) Schematic of Cdc12 with formin homology (FH) domains 1 and 2, armadillo repeats (ARM), oligomerization domain (C’), and Cdk1-targeted residues labeled. The Cdc15-binding motif (residues 24–36) is indicated by the black bar. T95, identified by Swaffer et al. (2016), is labeled with an asterisk. (C, D) Denatured cell lysates were prepared from the indicated mitotically arrested mts3-1 strains. Anti-HA immunoprecipitates of the samples were (C) subjected to lambda phosphatase treatment or buffer control or (D) incubated with MBP-Clp1, MBP-Clp1-C286S, or buffer control. Samples were resolved by SDS–PAGE and immunoblotted. CDK served as loading control. Brackets span phosphorylated species and asterisks mark hypophosphorylated species of Cdc12. (E) In vitro binding assay of bead-bound recombinant MBP, MBP-Cdc12(1–765), or MBP-Cdc12(1–765-6A) with recombinant Cdc15 F-BAR(19–312) incubated with either kinase active (KA) or kinase dead (KD) Cdk1–Cdc13. Uncropped images are in Supplemental Figure S2B. (F) In vitro binding assay of bead-bound recombinant MBP, MBP-Cdc12(1–765), MBP-Cdc12(1–765-6A), or MBP-Cdc12(1–765-6D) with recombinant Cdc15 F-BAR(19–312). Uncropped images are in Supplemental Figure S2C. (E, F) Samples were washed, resolved by SDS–PAGE, and stained with CB.