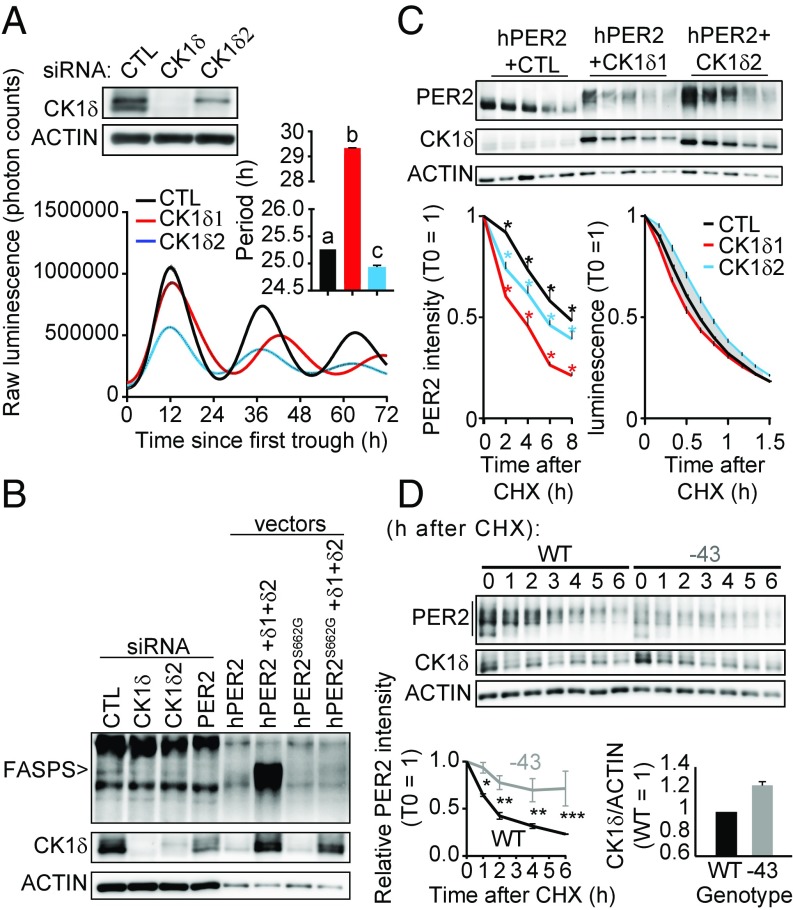
Fig. 5.
CK1δ2 stabilizes PER2 and slows the clock. (A) Silencing of Ck1δ2 leads to short period, while silencing of both Ck1δs leads to long period. Knock-down efficiency of Ck1δ and Ck1δ2 was first confirmed by immunoblotting (Top). Main graph shows mean ± SEM of real-time luminometry traces for each group; n = 2. (Right Inset) Mean period ± SEM analyzed by one-way ANOVA, P < 0.0001. a vs. b vs. c, at least P < 0.01 in Bonferroni post hoc. (B) Silencing of endogenous Ck1δ2 in human U-2 OS cells is sufficient to decrease FASPS phosphorylation, as identified by immunoblotting. The identity of the FASPS band was confirmed by transfection of mutated or wild-type expression vectors. (C) The stability of hPER2 phosphorylated by CK1δ2 is higher than that of CK1δ1-phosphorylated hPER2, measured in transiently transfected cells. Representative PER2, CK1δ, and ACTIN immunoblots are shown. (Bottom Left) Mean relative band intensity ± SEM of total PER2, analyzed by two-way ANOVA, all sources of variations at least P < 0.01, n = 3; *at least P < 0.05 in Bonferroni’s post hoc. (Bottom Right) The effect of CK1δs on PER2::LUC stability in the stably transfected cell lines used in Fig. 3E, showing mean relative luminescence ± SEM, analyzed by two-way ANOVA, with all sources of variations P < 0.0001, n = 6. The grayed area shows where significance reached P < 0.0001 between cell lines in Bonferroni’s post hoc test. (D) PER2 is more stable in −43/−43 primary adult skin fibroblasts than in wild type, consistent with higher CK1δ expression, represented mainly by CK1δ2 in these cells. The lower ACTIN signal from −43/−43 cells was due to lower cell counts at the time of sampling, i.e., mean ± SD, 3.68 ± 0.15 × 105 for −43/−43 cells versus 4.42 ± 0.27 × 105 for wild type. (Bottom Left) Quantification of the entire PER2 signal at 0, 1, 2, 4, and 6 h after CHX from n = 3 experiments and analyzed by two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. (Bottom Right) CK1δ/ACTIN signal ratio averaged across the entire time course shown above, with the relative intensity in wild type for each time point equal to 1.