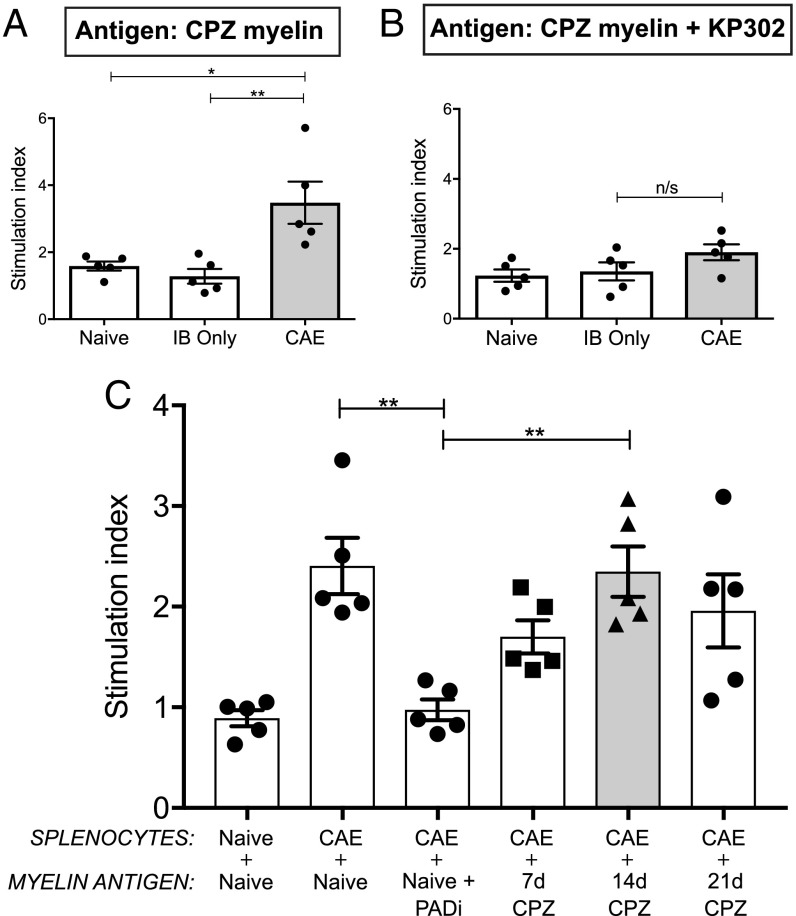
Fig. 4.
CAE splenocytes reacted robustly and specifically to donor myelin. (A) Relative to splenocytes from naive controls without added antigens, cells derived from animals at the peak of CAE proliferated in response to myelin isolated from donor CPZ mouse brains. (B) CAE splenocytes were unreactive to myelin derived from CPZ animals treated in vivo with KP-302. (C) CAE splenocytes also reacted to naive myelin but not when the same naive donors were treated in vivo with KP-302. The duration of CPZ treatment—tied to varying degrees of citrullination (SI Appendix, Fig. S4)—modulated the resulting responses of CAE splenocytes. Each dot represents the mean of three technical antigen replicates from a single mouse in which n = 5 mice for all splenocyte sources and n = 3–4 mice for myelin isolates. Significance was determined by one-way ANOVA. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01; n/s, not significant.