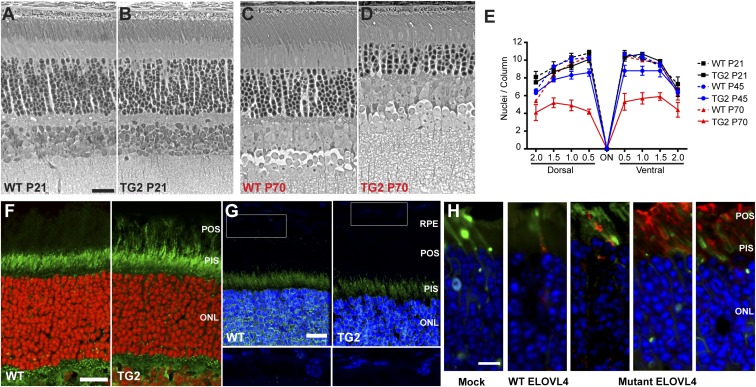
Fig. 1.
Retinal degeneration and localization of ELOVL4. (A–D) Phase-contrast images of semithin sections from P21 or P70 WT (A and C) and TG2 (B and D) retinas. Mutant TG2 retinas were similar in overall morphology to WT retinas at P21, but the photoreceptor cells have undergone markedly significant degeneration by P70, as can be observed by the loss of photoreceptor nuclei in the outer nuclear layer (ONL). (E) Graph of the number of photoreceptor nuclei per column in the ONL, quantified at 0.5-mm intervals from the optic nerve (ON). Some photoreceptor cell loss in TG2 retinas was observed at P45; by P70 it was more severe. (F and G) Retinal sections from P21 WT and TG2 mice immunolabeled with antibodies against the N-terminal (F) or C-terminal (G) region of ELOVL4 (green). The N-terminal antibody recognizes both WT and mutant ELOVL4, but the C-terminal antibody recognizes only WT ELOVL4. Photoreceptor outer segments (POSs) are labeled in the TG2 retinal section by the former (F), but not the latter (G). Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (shown as red or blue). Lower panels (G) represent higher magnification of rectangles in Upper panels, with the brightness of the blue channel increased to make weaker DAPI staining of RPE cells visible. (H) Retinal sections from mice whose photoreceptors were electroporated with Dendra2 (green) and FLAG-tagged WT or mutant human ELOVL4 plasmids. The sections were labeled with a FLAG antibody (red). Mock retinas were electroporated with Dendra2 only. The WT FLAG-ELOVL4 protein is localized primarily to the photoreceptor inner segment (PIS). The three panels to the Right are examples from different experiments with the mutant FLAG-ELOVL4; protein was observed mostly in the POS, with some presence in the PIS (mutant ELOVL4 still contains the N-terminal ER localization signal, but it has lost the C-terminal ER retention signal). (Scale bars: 10 μm in A, F, and H, and 15 μm in G.)