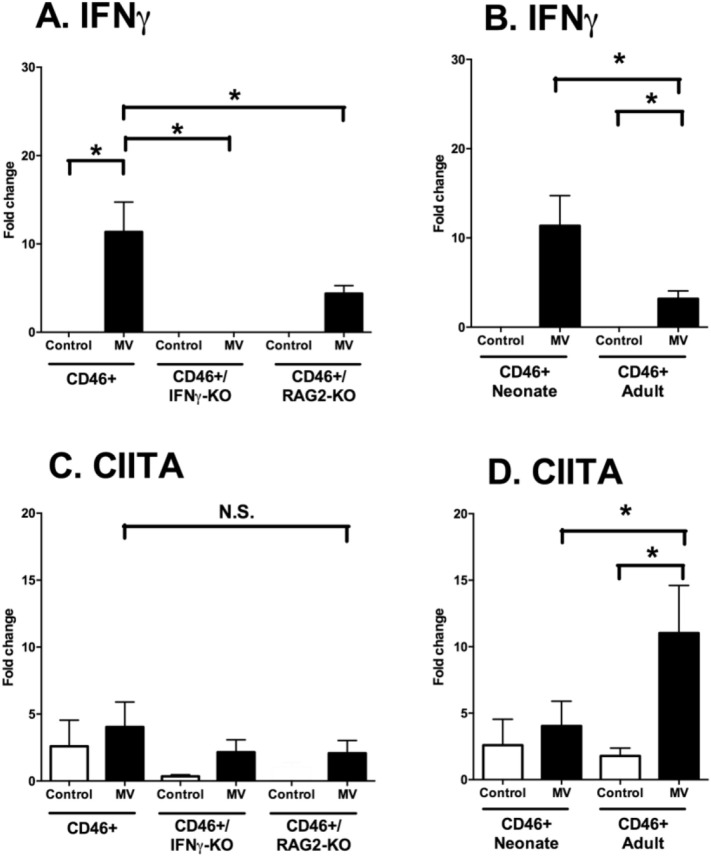
Fig. 9.
Despite elevated IFNγ expression during infection, transcription of IFNγ-responsive genes is age-dependent.
Brains of uninfected and MV-infected CD46+ mice were analyzed for the mRNA expression of IFNγ and CIITA at 7 dpi. CD46+, CD46+/IFNγ-KO, and CD46+/RAG2-KO neonates (left column; A, C) and CD46+ neonates and adults (right column, B, D) were compared. qRT-PCR analysis was performed for IFNγ (A, B) and CIITA (C, D). Relative gene expression is shown as the fold-change normalized to the CD46+ uninfected controls (n = 4–5 mice/condition). Each bar represents the mean fold-change and SEM. Statistical differences were determined by two-way ANOVA (*p < 0.05, #p < 0.001) with Bonferroni post hoc test.