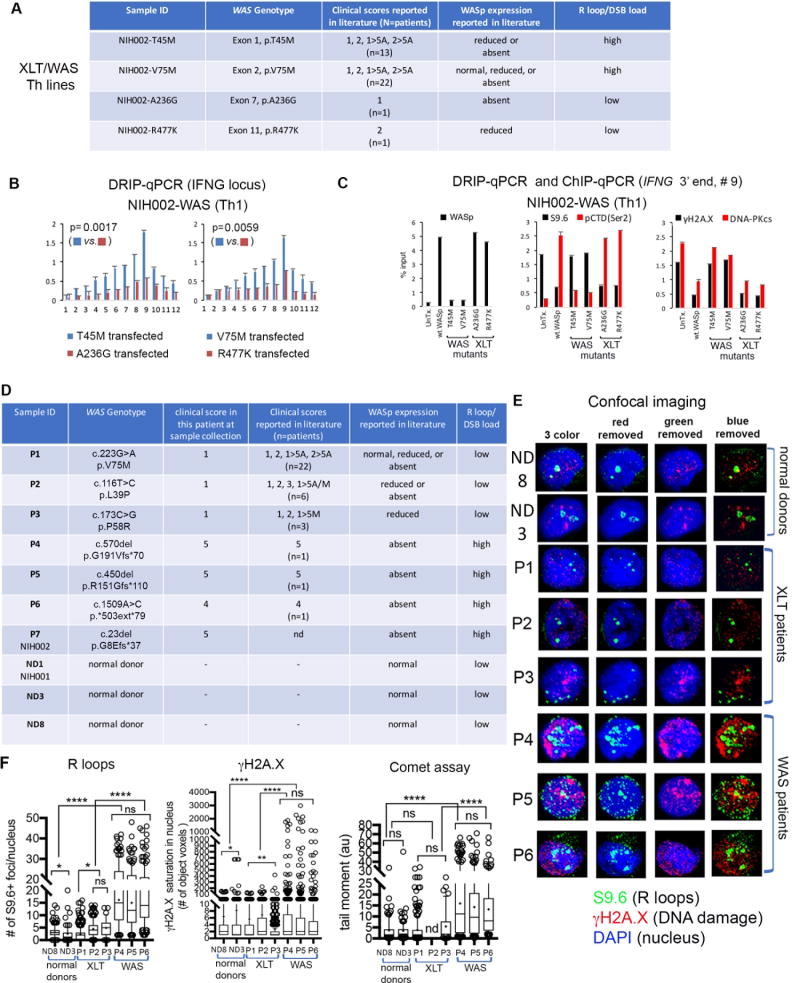
Figure 7. R-loop and DNA-damage levels in Th1 cells correlate with disease-severity scores in WAS-XLT spectrum.
(A) The table shows 4 disease-causing WAS-mutations engineered in vitro for stable transfection into NIH002-WAS-null T-cell line to generate Th-lines representative of mutations that associate with mild or severe clinical phenotypes, as shown. Clinical-severity: score-1, 2: mild-XLT with eczema; score-5A, -5M, severe immunodeficiency with autoimmunity (A) or malignancy (M); 1, 2→5A/5M denotes disease progression to severe WAS after initially presenting as XLT in the same patient.4-6,86 (B) R-loop frequency across the IFNG-locus in NIH002-WAS Th1-line stably-expressing indicated WASp-mutants. p-values by Wilcoxon nonparametric test. (C) ChIP and DRIP (S9.6) enrichment profiles of indicated factors at 3′-end of IFNG (point #9, Figure 1E) in the indicated mutant. n=3, mean +SEM. (D) The table shows genotype-phenotype characteristics of pathogenic mutations in patients from whom primary Th cells (P1-P6) and a Th cell line (P7), as well as Th cells from normal donors (ND1, ND3, ND8) were generated.10,61(E) A representative confocal-image (a collapsed composite of multiple z-stack planes) for each patient and donor T-cell sample shows their respective R-loop load (S9.6+ foci) and DSB load (γH2A.X and neutral comet assay). (F) Box-and-whisker plots (whisker@ 10-90%), calculated on z-stacks (n=20-30 stacks/cell) from n=120-190 cells (exception: n=33 cells analyzed for patient-P2 due to small sample volume) for indicated read-outs. S9.6+ foci, γH2A.X signal-saturation in the nucleus, and comet tail moment were processed and quantified using ImageJ 2.0 and Prism7 programs. Entire multi-cell images were optimized equally by Adobe Photoshop to reduce any background fluorescence (“signal-noise”). ***p<0.0001, *p=0.01, ns= nonsignificant, p>0.1 by two-tailed non-parametric Mann-Whitney.