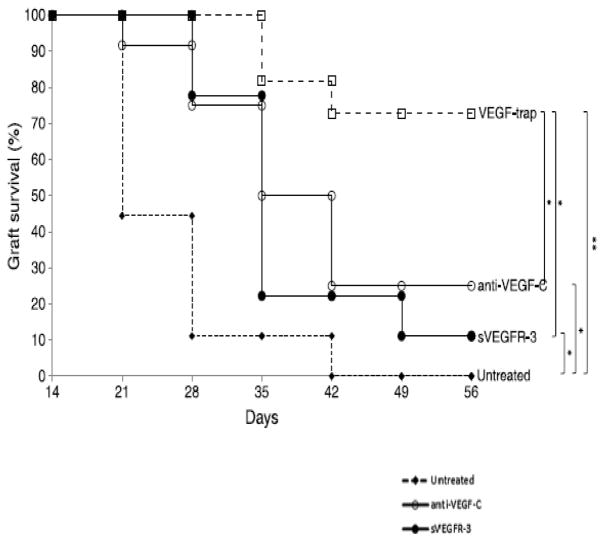
Figure 13.
Effect of VEGF neutralization on high-risk corneal transplant survival. Animals underwent high-risk allogeneic corneal transplantation and received treatment with anti-VEGF-C, sVEGFR-3, or VEGF-trap at the time of transplantation, at 3, 7, 10, and 14 days after transplantation, and then once per week for an additional 6 weeks, or they remained untreated. The VEGF-trap treatment was most effective in increasing allograft survival (72%), though treatment with anti-VEGF-C (25%) and sVEGFR3 (11%) also significantly improved survival compared to that in the untreated control group. To create the Kaplan-Meier survival curve, graft opacity was evaluated according to an established 0 to 5+ scale by slit-lamp biomicroscopy. Scores greater than or equal to 2+ are considered rejected. Each group consisted of n=9–12 mice. **P < 0.005, *P < 0.05, error bars represent standard error of the mean (SEM). Data from one experiment of two are shown. 56 (Adapted from Dohlman et al with permission from Wolters Kluwer)