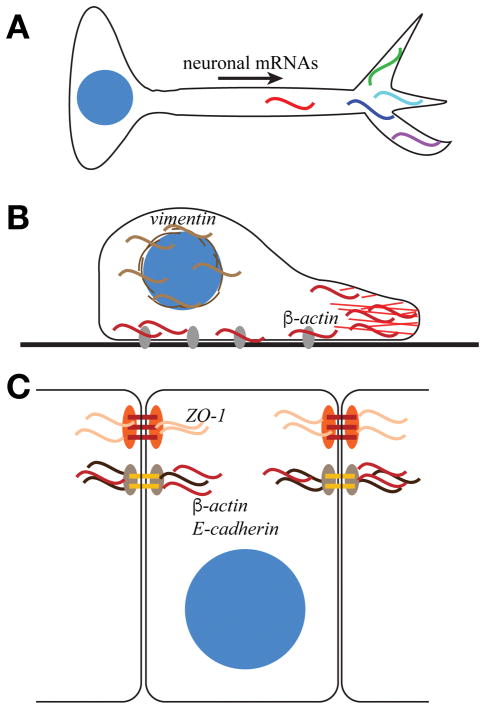
Figure 1. RNA localization within polarized cells.
(A) Multiple mRNAs (colored sinusoidal lines) localize to neuronal processes and contribute to neuronal polarization and function. (B) In migrating fibroblasts, β-actin mRNA (red) localizes to the leading edge of cells and to FA plaques (grey ovals), while vimentin mRNA (brown) is enriched at the perinuclear domain. β-actin localization and translation at focal adhesions contributes to the regulation of adhesion and migration. (C) In epithelial cells, β-actin and E-cadherin mRNAs localize to adherens junctions, whereas zonula occludens-1 mRNA (ZO-1) localizes to tight junctions to regulate cell adhesion.