Figure 3. KD-Associated Bacteria Sufficiently Mediate the Anti-Seizure Effects of the Ketogenic Diet.
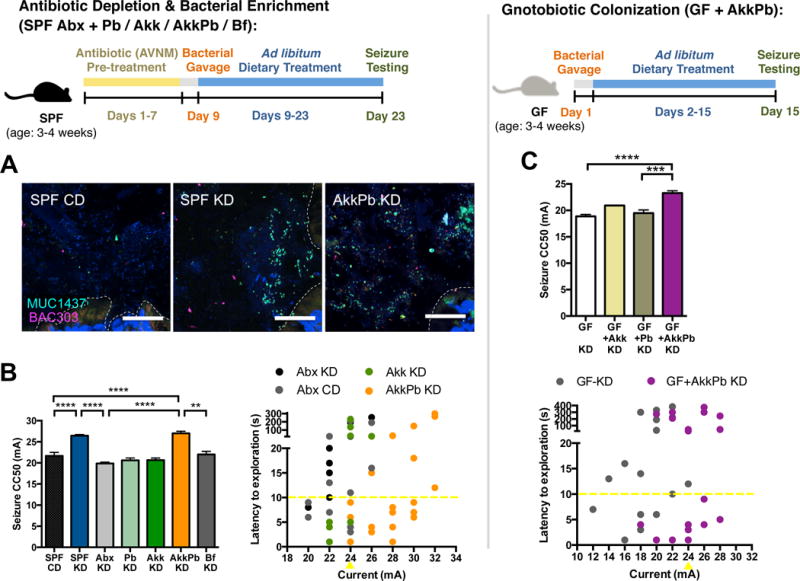
(A) Fluorescence in situ hybridization for A. muciniphila (MUC1437) and select Bacteroides and Parabacteroides, including P. merdae and P. merdae (BAC303) in colonic lumen from SPF mice fed CD, SPF mice fed KD or A. muciniphila and Parabacteroides-enriched mice fed KD. Scale bar = 25 um. Dotted lines indicate the borders of the intestinal epithelium. n = 3.
(B) Seizure thresholds in response to 6-Hz stimulation in SPF mice pre-treated with vehicle or Abx, and colonized with Parabacteroides, Akkermansia muciniphila, both, or Bifidobacterium longum (left). n = 13, 18, 15, 6, 8, 5, 5. Behavior in representative cohort of seizure-tested mice (right). Yellow line at y=10 seconds represents threshold for scoring seizures, and yellow triangle at 24 mA denotes starting current per experimental cohort. n = 12, 16, 8, 25.
(C) Seizure thresholds in response to 6-Hz stimulation in GF mice colonized with Parabacteroides and/or A. muciniphila (top). n = 15, 4, 9, 9. Behavior in seizure-tested mice (bottom). n = 17, 19.
Data are presented as mean ± SEM. One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni: **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. SPF=specific pathogen-free, GF=germ-free, CD=control diet, KD=ketogenic diet, CC50=current intensity producing seizures in 50% of mice tested, veh=vehicle, Abx=pre-treated with antibiotics (ampicillin, vancomycin, neomycin, metronidazole), Pb=Parabacteroides (P. merdae and P. distasonis), Akk=Akkermansia muciniphila, AkkPb=A. muciniphila, P. merdae and P. distasonis, Bf=Bifidobacterium longum. See also Figure S3.
