Figure 3. C-terminal glycine correlates with protein instability and is depleted from eukaryotic proteomes.
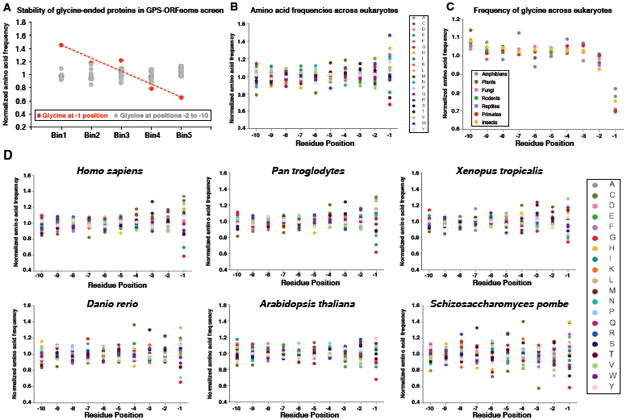
(A) C-terminal glycine correlates with instability: ORFs terminating in glycine are enriched in Bin1 and depleted from Bin5. Glycine at the terminal (-1) position is depicted in red, while glycine at all other positions in the last ten residues is shown in gray.
(B) Normalized amino acid frequencies across the last ten residues of eukaryotic proteins.
(C) Normalized frequency of glycine across the last ten residues of proteomes from the indicated taxa.
(D) Amino acid proportions across the last ten positions of each proteome are shown. The data for each residue are normalized to the mean proportion across the last ten positions.
