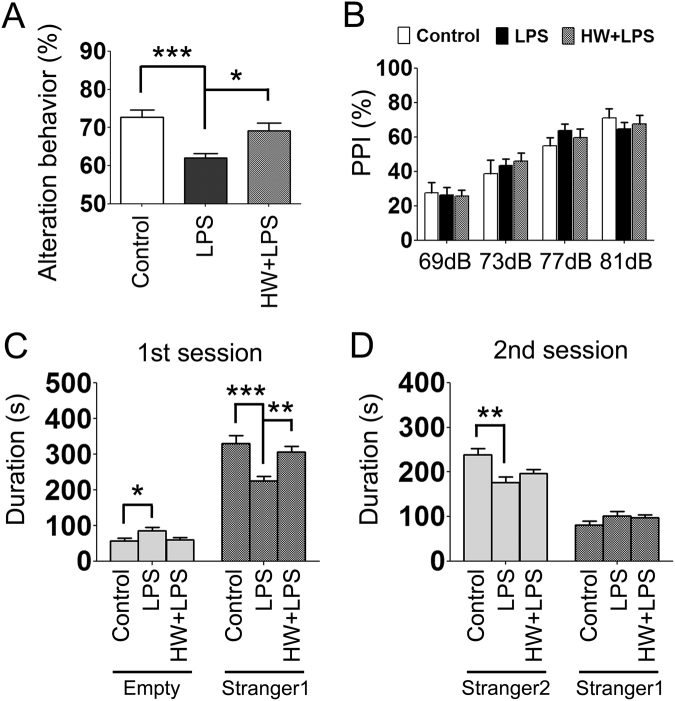
Figure 2.
Effects of LPS and H2 on the acquisition of short-term recognition memory in the Y-maze test (A) PPI test (B) and sociability and social novelty preference (C,D). (A) In the LPS group, short-term recognition memory was significantly impaired. In the HW + LPS group, maternal administration of hydrogen water almost completely restored short-term recognition memory. (B) No significant difference was detected in each trial. (C,D) Means ± standard error of the mean are shown for the cumulative data over each 10-min test session. (C) Time spent within the sniffing zone of the wire cage containing the novel mouse; Stranger 1, or the empty wire cage. (D) Time spent within the sniffing zone of the wire cage containing the familiar mouse; Stranger 1, or Stranger 2 (n = 17–22; Control, 17 pups/5 dams; LPS, 22 pups/5 dams; HW + LPS, 19 pups/5 dams). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001; by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s honest significant difference test. LPS, lipopolysaccharide; HW, hydrogen water.