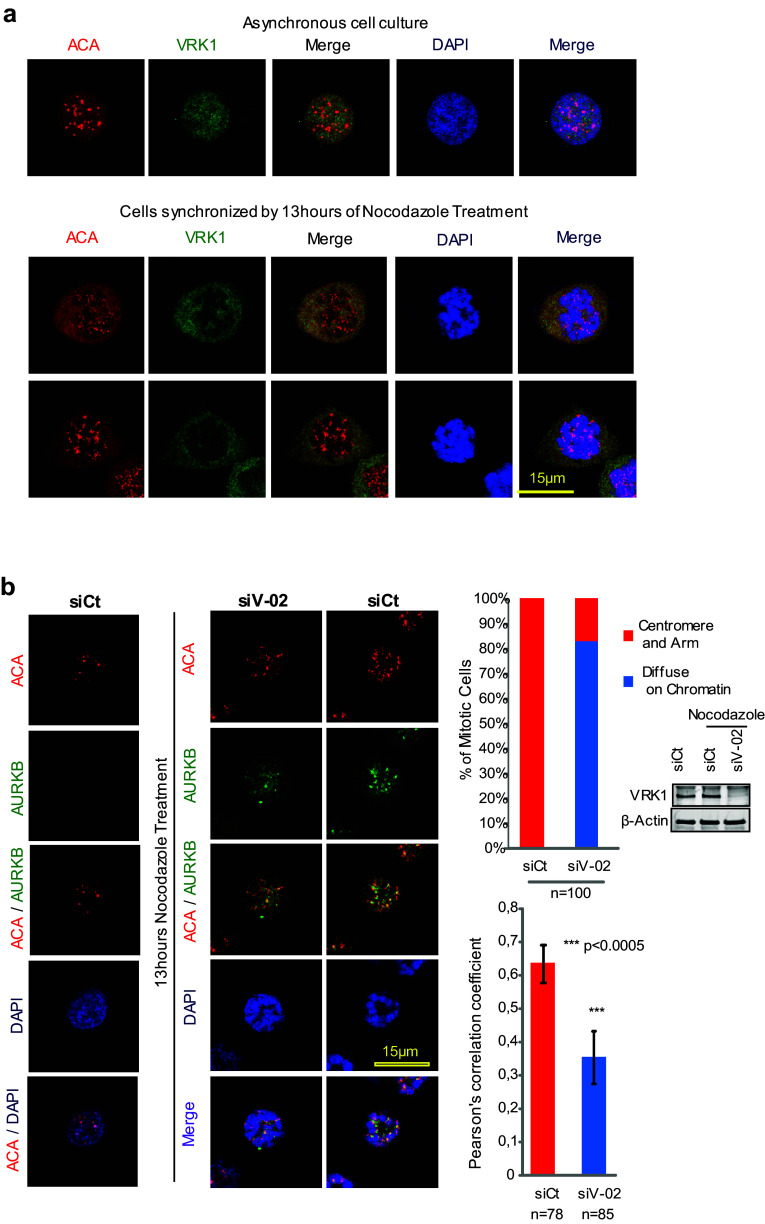
Fig. 6.
Effect of VRK1 on the centromeric localization of AURKB and ACA. a VRK1 in U2OS cells does not colocalize with ACA in non-synchronic cells (top panel) or in cells synchronized and arrested with nocodazole (bottom panel). b Colocalization of AURKB and ACA on centromeres is affected by the knock down of VRK1, indicating that it interferes with centromere recruitment. The U2OS cells were treated during 13 h with nocodazole. AURKB was detected using a rabbit monoclonal anti-AURKB antibody and ACA was detected using a human anti-ACA antibody. Immunofluorescence experiments were performed three times. The number of cells is indicated in the figure (additional individual cells are shown in Supplementary Figure S6). The quantification of the AURK and ACA signals, and the DAPI signal (DNA) were quantified with the confocal software and their overlap is shown in the graphs to the right. A total of 100 cells were counted taking into account the distribution of AURKB on centromeres and chromosome arm or diffused on the chromatin (Chi-square statistic is significant at P < 0.01). Colocalization studies were performed by two distinct methods: the first by analyzing the images and the distribution of AURKB on centromeres and chromosome arms, or diffused on the chromatin, and the second calculating the Pearson’s correlation coefficient value separately for each cell. This coefficient gave us the value of overlapped red and green pixel in each cell. The Pearson’s correlation coefficient value was calculated separately for each cell, giving the value of overlapping red and green pixels in each cell (Student’s test: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.005, ***P < 0.0005). To the right is shown the reduction in the level of VRK1 after its knockdown by immunoblot