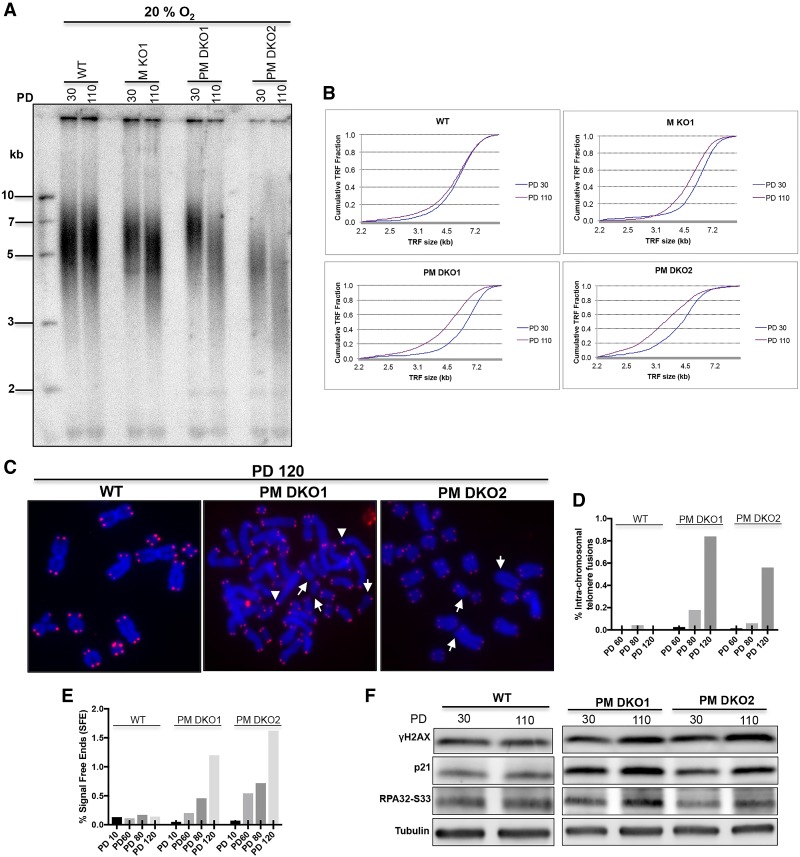
Figure 5.
MTH1–PRDX1 double knockouts accumulate extremely short telomeres and DNA damage markers. (A) TRF analysis at PD30 and PD110. The indicated clones were grown in incubators containing 20% O2. (B) Distribution profile of telomere fragments at the indicated PDs of A. (C) Analysis of telomere signals (red) in metaphase chromosomes (blue) of clones grown for 120 PDs. White arrows indicate telomere signal-free ends, and arrowheads indicate intrachromosomal telomere fusions. (Blue) DAPI-stained chromosomal DNA; (red) TeloC probe for telomeric DNA. (D) Quantification of intrachromosomal telomere fusions. (E) Quantification of telomere-free ends across different PDs. (F) Western blot analysis of DNA damage markers in PRDX1/MTH1 double-knockout (PM DKO) cells grown for 30 and 110 PDs. For D and E, >2700 telomeres were scored for each sample.