Figure 4.
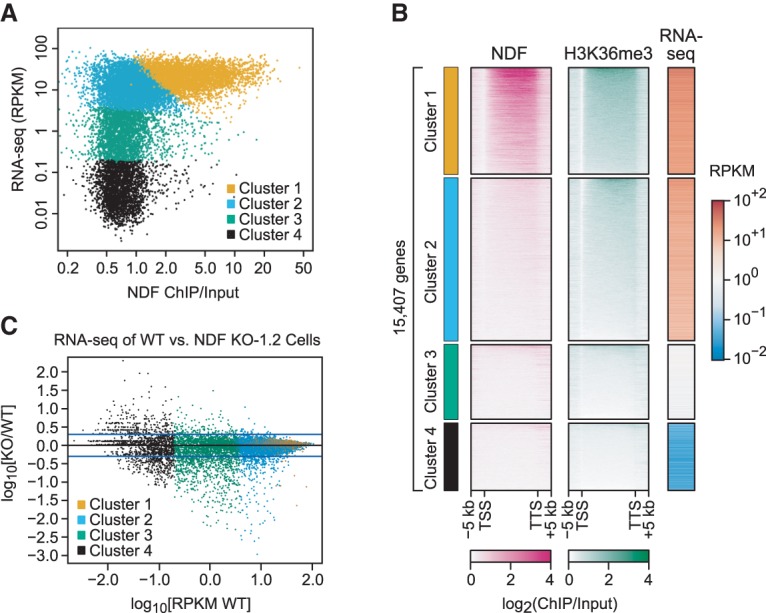
NDF contributes to the expression of many genes. Four clusters of genes were generated by k-means clustering with three variables: log10[RNA-seq signal of genes in RPKM] (reads per kilobase per million mapped reads), log10[(NDF ChIP-seq signal over gene body)/(input signal over gene body)], and log10[(H3K36me3 ChIP-seq signal over gene body)/(input signal over gene body)]. (A) NDF is enriched in active gene cluster 1 but not in active gene cluster 2. RNA-seq signal (RPKM) versus NDF ChIP/input signal for gene clusters 1–4. (B) Heat maps of NDF and H3K36me3 occupancies and gene expression in wild-type HeLa cells. Genes within each cluster were ranked by the (NDF ChIP-seq signal)/(input signal) ratio. (C) RNA-seq analysis of wild-type versus hNDF KO-1.2 cells. The plot shows log10[(RPKM knockout)/(RPKM wild type)] versus log10[RPKM wild type] for genes in clusters 1–4. Genes with RPKM = 0, such as those in cluster 4, were not included in this analysis. The top and bottom blue lines correspond to (RPKM knockout)/(RPKM wild type) ratios of 2 and 0.5, respectively.
