Figure 4.
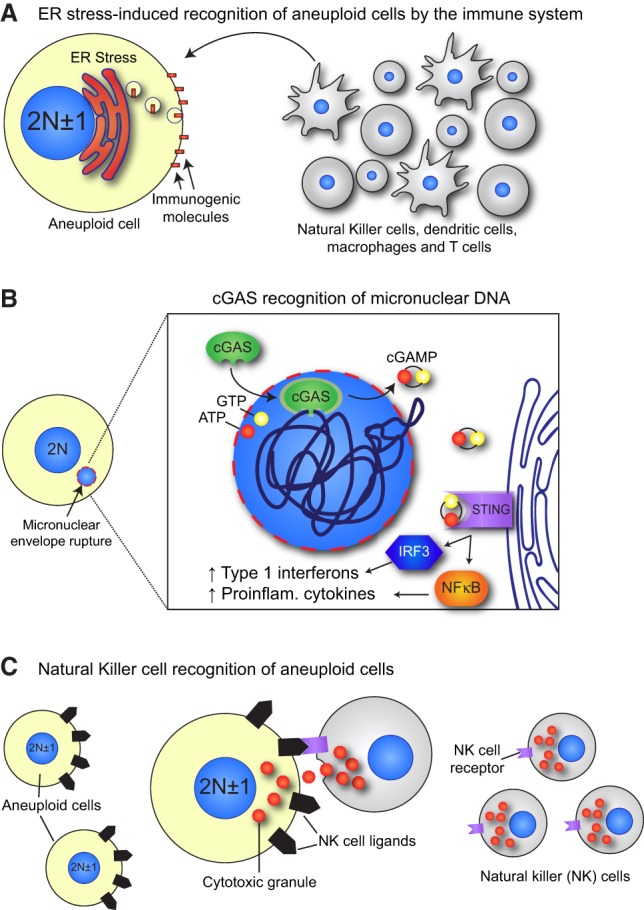
Mitotic errors activate the immune system. (A) Aneuploid cells exhibit a constitutive endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress that leads to the increased surface exposure of immunogenic cell surface molecules, such as calreticulin. These are recognized by immune cells such as natural killer (NK) cells, dendritic cells, macrophages, and T cells that engulf or kill the aneuploid cell. (B) The micronuclear envelope is prone to rupture, leading to the exposure of the entrapped chromatin to cytoplasmic DNA-sensing molecules, such as cGAS. cGAS is activated by the exposed micronuclear DNA, allowing for conversion of ATP and GTP to the second messenger cGAMP. cGAMP activates STING, which causes IRF3- and NFκB-mediated expression of type 1 interferons and proinflammatory cytokines, respectively. (C) Aneuploid cells exhibit increased expression of NK cell-activating ligands, which allow recognition and killing of aneuploid cells by NK cells through their NKG2D and DNAM1 receptors.
