Fig. 2.
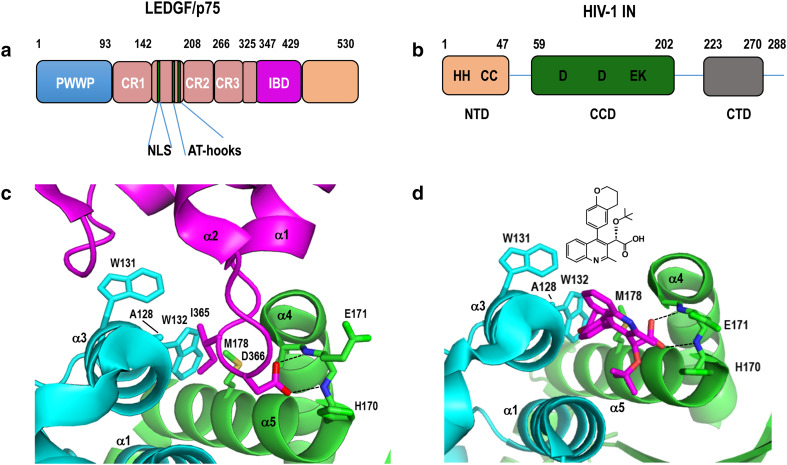
LEDGF/p75 and ALLINI structures and binding to integrase. a Schematic diagram of LEDGF/p75, highlighting different protein regions/domains. Chromatin binding is mediated by the PWWP domain, charged regions (CR) 1–3, two copies of an AT-hook DNA binding motif, and basic NLS [95, 96]. CR 2 and 3 confer binding to supercoiled DNA [97]. Numbers refer to domain boundary positions. b Schematic of HIV-1 integrase; numbers demarcate domain boundaries. Amino acids invariant across Retroviridae are indicated by single-letter code. c X-ray structure of the LEDGF/p75 IBD (magenta) bound at the HIV-1 integrase CCD dimer (cyan and green). Shown in sticks are LEDGF/p75 hotspot residues Ile365 and Asp366 as well as integrase residues that help mold the binding pocket. Dashed lines, hydrogen bonds. Blue, red, and yellow denote nitrogen, oxygen, and sulfur, respectively (protein database (PDB) accession code 2B4J [102]). d X-ray structure of ALLINI BI-D (magenta, with chemical structure shown above) bound to the integrase CCD dimer (PDB code 4ID1 [190]), oriented as in c. The carboxylic acid attached to position 3 of the quinoline ring via the tert-butoxy group makes the same hydrogen bond contacts with integrase (dashed lines) as LEDGF/p75 residue Asp366 (compare with c). Other labeling is as in c