Figure 1. Regulation of Deptor expression by Wnt/β-catenin signaling.
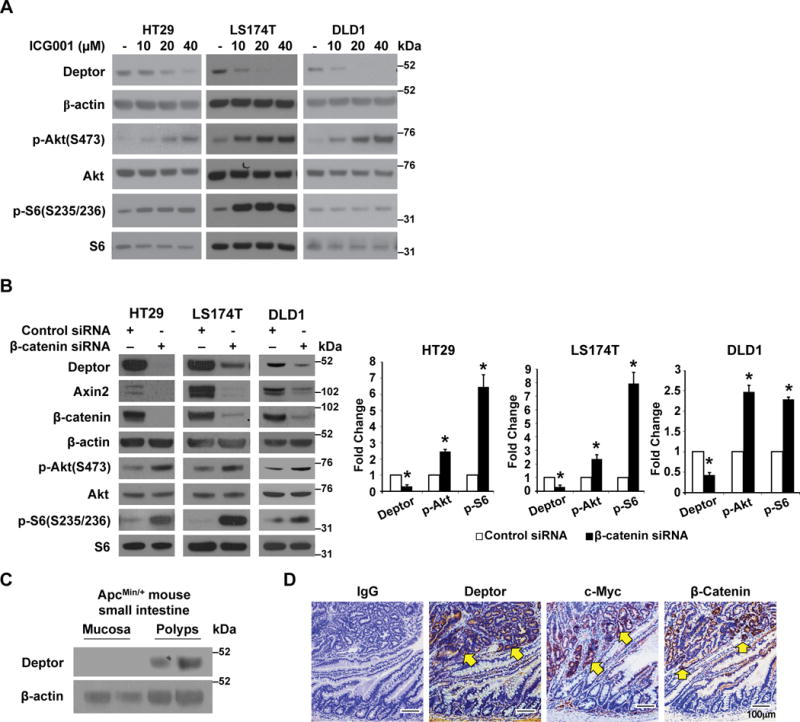
A. Inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin signaling decreases Deptor protein expression. Treatment with Wnt inhibitor ICG001 decreased Deptor expression. LS174T, HT29, and DLD1 cells were treated with Wnt inhibitors ICG001 for 24 h. Cells were lysed and western blot analysis was performed using antibodies against Deptor, p-Akt, Akt, p-S6, S6, and β-actin. The images are representative of three independent experiments. B. Knockdown of β-catenin results in the induction of mTOR activation and a decrease of Deptor protein expression. HT29, LS174T and DLD1 cells were transfected with β-catenin or non-targeting control siRNA. After 48 h incubation, transfected cells were lysed and western blot analysis was performed using antibodies against Deptor, Axin2, β-catenin, β-actin, p-Akt, Akt, p-S6 and S6. The images are representative of three independent experiments. Deptor, p-Akt and p-S6 signals from three separate experiments were quantitated densitometrically and expressed as fold change with respect to β-actin, total Akt or total S6, respectively. (n= 3, data represent mean±SEM; *P<0.01 versus control siRNA). C&D. Activation of Wnt signaling increases Deptor expression. Tumors of ApcMin/+ mice show increased expression of Deptor (C). Western blots of extracts from either normal intestine mucosa or a pool of polyps from the small intestine of ApcMin/+ mice (n=2). Representative IHC staining of Deptor, c-Myc and β-catenin in polyp and adjacent normal ileum (D). Scale bars, 100 μm.
