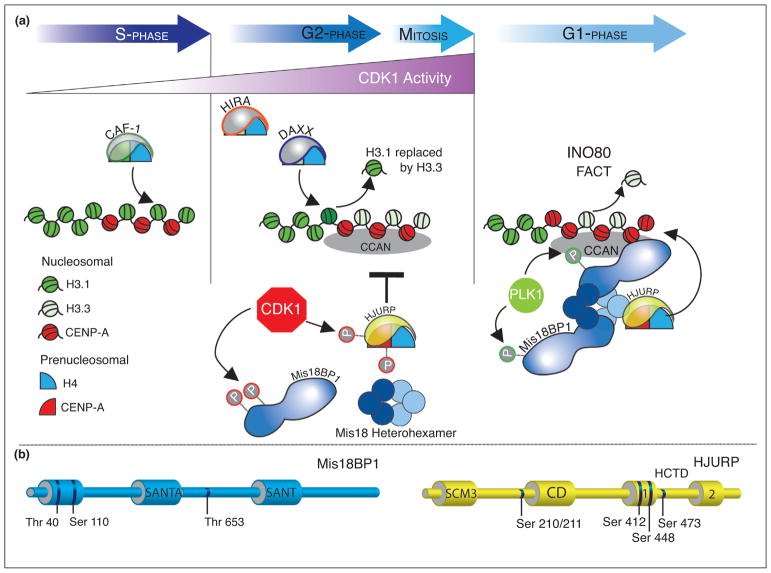
Figure 3.
Cell cycle control of vertebrate CENP-A deposition. (a) CDK1 activity increases in G2/M phase and inhibits the deposition of CENP-A nucleosomes by directly phosphorylating Mis18BP1 and the CENP-A chaperone HJURP. Mis18BP1 phosphorylation disrupts the binding to the Mis18α/β oligomer and thus inhibits recruitment of the complex to centromeres. Reduction of CDK1 activity in response to activation of the APC/C following mitotic checkpoint satisfaction leads to CENP-A deposition in G1. PLK1 activity positively regulates CENP-A deposition through phosphorylation of Mis18BP1. FACT mediated transcription in Drosophila and INO80 remodeling complex in budding yeast promote histone exchange within centromeric chromatin (reviewed by [70]). (b) CDK1 targeted phosphorylation sites within Mis18BP1 and HJURP that are known to inhibit CENP-A deposition are depicted.