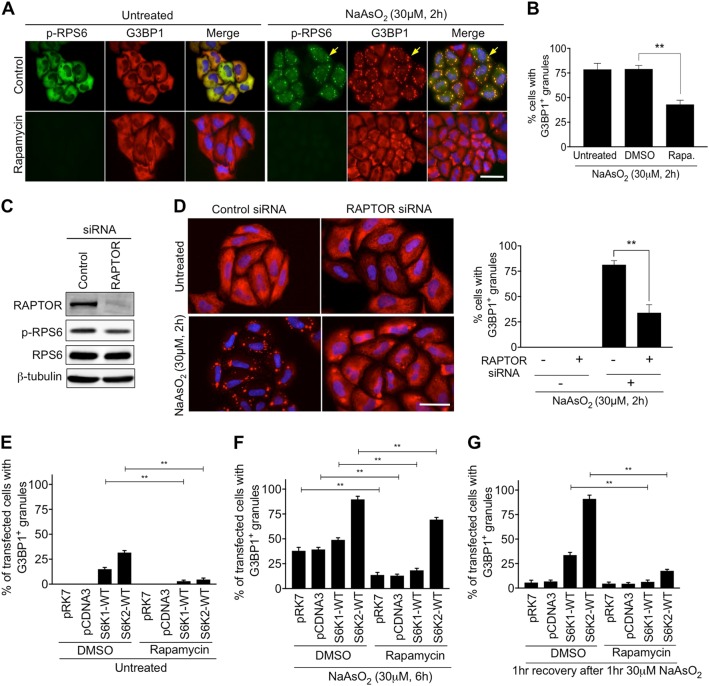
Fig. 4.
The mTORC1-S6K signalling pathway is required for stress granule assembly. a HeLa cells were pre-treated with 50 nM Rapamycin for 2 h prior to exposure to 30 μM NaAsO2 for a further 2 h. Cells were immunostained for G3BP1 (red) and the phosphorylated form of RPS6 (p-RPS6) (green). Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Yellow arrows indicate examples of stress granules. Scale bar = 25 μm. b Quantification of cells forming stress granules under the indicated conditions. c HeLa cells were subjected to siRNA directed against RAPTOR. Immunoblots of cell extracts with antibodies to RAPTOR, phosphorylated RPS6 (p-RPS6), RPS6 and β-tubulin are shown. d Images of cells treated with or without 30 μM NaAsO2 for 2 h and subjected to RAPTOR siRNA. Cells were immunostained for G3BP1 (red). Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar = 50 μm. Quantification of cells forming stress granules under the indicated conditions is presented. e–g Cells expressing S6K1p70 or S6K2p54 were pre-treated with DMSO or rapamycin for 2 h and then subjected to either 30 μM NaAsO2 for a further 6 h (f) or 30 μM NaAsO2 for 1 h and left to recover for 1 h (g). For all quantifications, 100 cells per condition were counted in each of the 3 biological repeats. Error bars are s.e.m. Data were analysed using one-way Anova (**p < 0.0002)