Fig. 7.
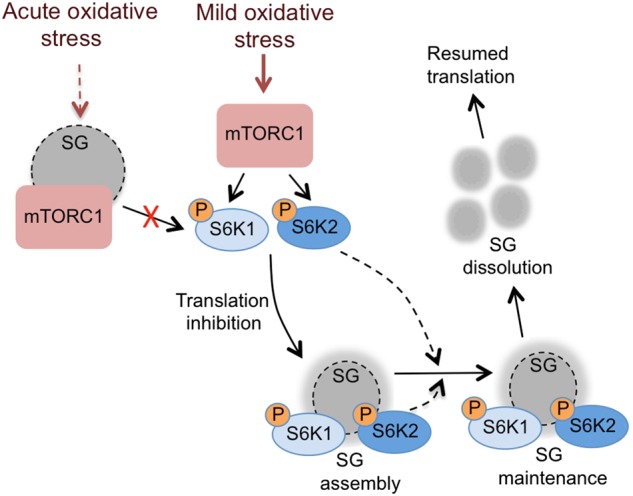
Schematic of the role of the mTORC1-S6 kinase pathway in stress granule assembly and maintenance. Distinct types of stress granule (SG) are formed depending on the level of oxidative stress. In response to acute oxidative stress, mTORC1 components are sequestered into solid SGs thus inhibiting mTORC1 activity [22, 23]. In response to mild oxidative stress, mTORC1 activates S6 kinases leading to inhibition of translation and the assembly of SGs that contain a solid core surrounded by a liquid shell. Both S6K1 and S6K2 can accumulate in SGs and S6K2 helps maintain SGs via an unknown mechanism. On recovery from the stress, the SGs dissolve and protein translation resumes
