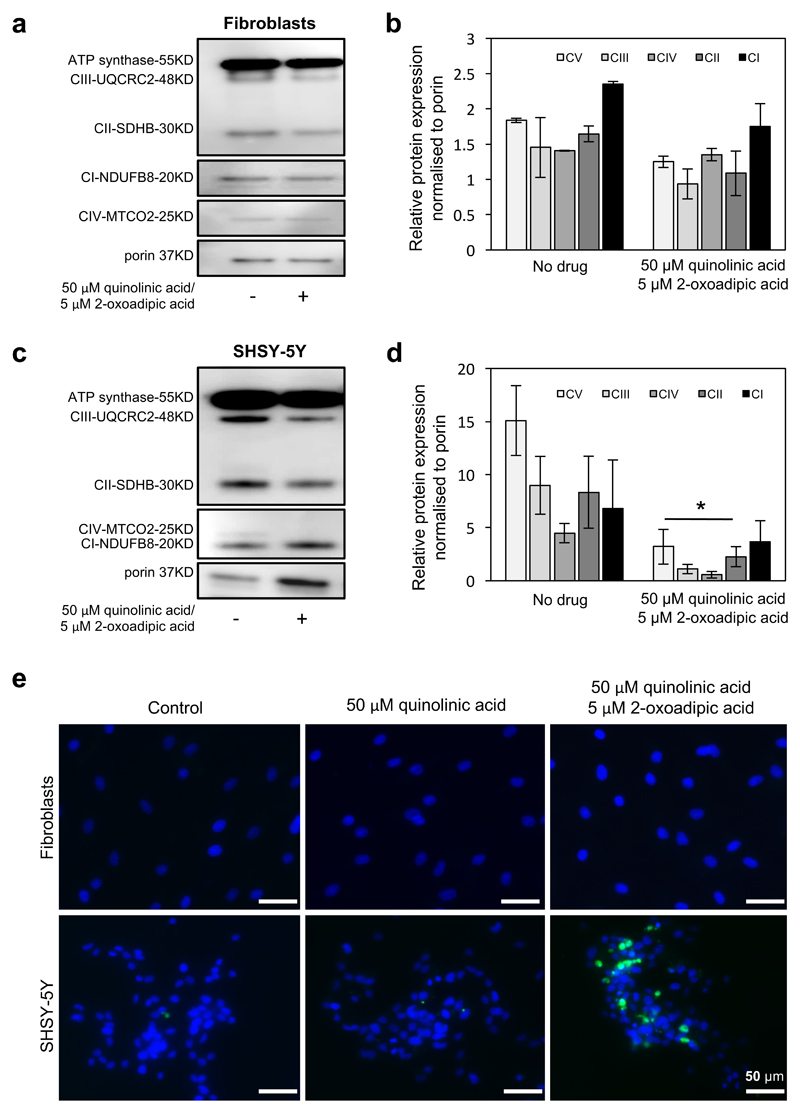
Figure 5. Administration of 2-oxoadipate and quinolinic acid in vitro was more toxic for neuronal cells than fibroblasts.
(a) Western blot analysis detected normal expression in control fibroblasts after supplementation of 50 μM quinolinic acid and 5 μM 2-oxoadipate after 4 days. (b) Quantification of protein levels were normalised to porin. (c) In human neuroblastoma cells (SHSY-5Y) the supplementation of the 50 μM quinolinic acid and 5 μM 2-oxoadipate resulted in significantly reduced levels affecting all five OXPHOS complexes, as shown in (d) (n=3 experimental replicates). P values are from One-Way ANOVA test. Where indicated * P<0.05. (e) Visualization of apoptotic cells stained with annexin V-FITC using confocal microscopy after treatment with only 50 μM quinolinic acid and combination of 50 μM quinolinic acid and 5 μM 2-oxoadipate. Cells were supplemented for 4 days before staining. DAPI staining was used as nuclear marker. Top row shows fibroblasts where no Annexin V positive cells were detected in any treatment. Bottom row shows SHSY-5Y cells: Indication annexin V positive cells were identified after double supplementation. Scale bar = 50μM.