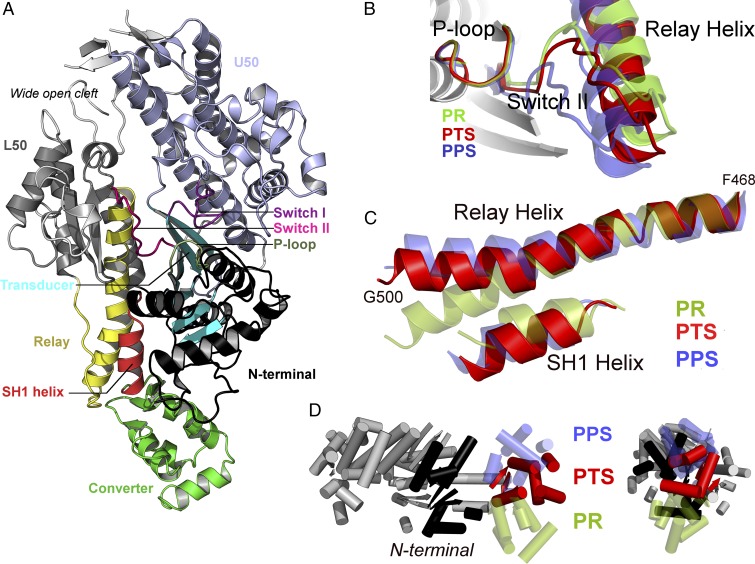
Fig. 2.
The PTS crystal structure reveals original structural features consistent with an on-pathway intermediate of the recovery stroke. (A) General view of the PTS crystal structure of myosin VI. For clarity, the SH3 motif is not represented. (B) Switch II adopts an open position closer to PR than PPS. A global movement of the Relay helix, i.e., the seesaw motion proposed by Fischer et al. (15), is also required to reach PPS. (C) Comparison of the Relay and SH1 helices. Unlike in PR, the Relay helix exhibits a kink and the SH1 helix is tilted downward. However, the orientation of the postkink fragment in the Relay helix and the degree of tilting of the SH1 helix differ from PPS. (D) The converter adopts an intermediate position between PR and PPS.