Fig. 3.
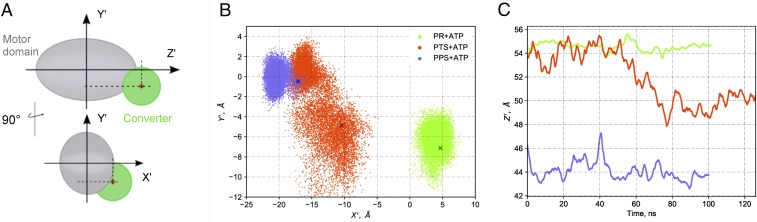
Positional dynamics of the converter in MD. (A) Geometric observables to monitor the position of the converter in simulation. By projecting the center of geometry of the converter Cα atoms on the principal axes of the motor domain, the components X′, Y′, and Z′ provide a convenient representation of the converter position relative to the motor domain; see SI Appendix for details. (B) Positional dynamics of the converter on the transverse plane X′Y′. Data points for PTS correspond to the first 125 ns; see SI Appendix, Fig. S3 for the complete data. Crosses indicate the crystallographic values. The data show the existence of two positional states for the converter in PTS: one widely distributed and centered on (−12 Å, −6 Å) and one more confined and in slight overlap with PPS centered on (−15 Å, 0 Å). (C) Time series of the Z′ component. The decrease in Z′ starting at t = 50 ns in the PTS simulation corresponds to a partial repriming toward the PPS position. For clarity, the running average over 2 ns is plotted.