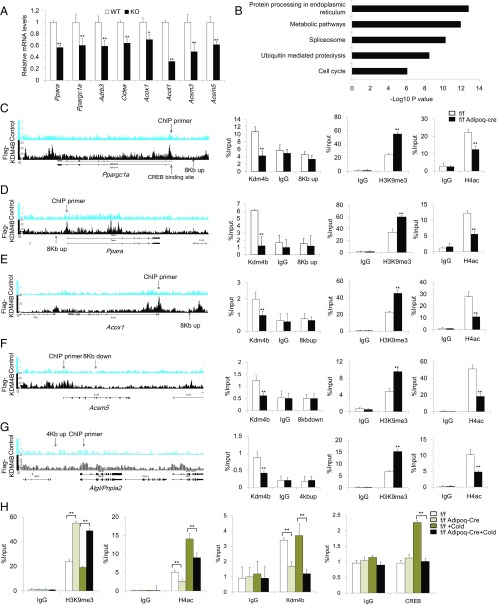
Fig. 6.
Loss of KDM4B leads to increased H3K9me3 and decreased H4ac to the metabolic genes promoter. (A) Relative mRNA levels of Ppara, Ppargc1a, Adrb3, Cidea, Acox1, Acot1, Acsm3, and Acsm5 in differentiated Kdm4b WT and KO adipocytes. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM. (B) KEGG pathway analysis of Kdm4b direct targets identified by ChIP-Seq. (C–G) The ChIP-Seq result, location of ChIP primers, determination of Kdm4b occupancy, the level of H3K9me3, and the levels of H4ac on the promoters of Ppargc1a, Ppara, Acox1, Acsm5, and Atgl in Epi WAT of 2-mo-old Kdm4bf/f and Kdm4bf/f Adipoq-Cre mice measured by ChIP-qPCR. Error bars represent mean ± SD for triplicate experiments. (H) The level of H3K9me3, H4ac, KDM4B occupancy, and CREB binding on the promoter of Ppargc1a before and after cold treatment in 2-mo-old Kdm4bf/f and Kdm4bf/f Adipoq-Cre mice. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01. Error bars represent mean ± SD for triplicate experiments.