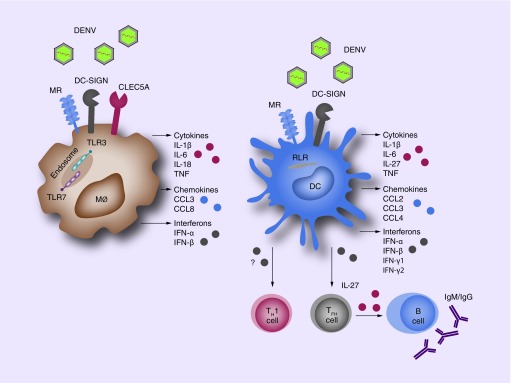
Figure 1. . Innate Immune receptors drive dengue immune activation.
Innate recognition of DENV is mediated by cell surface CLRs, TLRs and RLRs, which are mainly expressed by macrophages and dendritic cells. Activation of these receptors leads to the production of cytokines, chemokines and interferons that result in DENV immune activation. In addition to local effects, DCs activate T cells in secondary lymphoid tissues, which induce systemic immune responses. Notable, DENV-infected DCs drive T-helper 1 (TH1) differentiation. DCs also affect B-cell responses by instructing naïve T-helper cells towards follicular T-helper (TFH) cell differentiation by the production of IL-27. These cells induce B-cell proliferation, antibody production and isotype class switching.
DC: Dendritic cell; DENV: Dengue virus; MØ: Macrophage; MR: Mannose receptor.