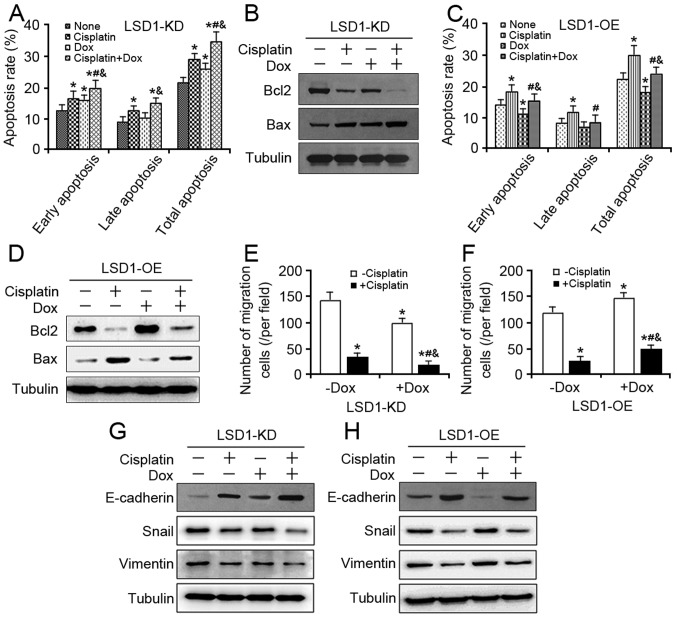
Figure 4.
Effects of LSD1 on cell apoptosis and migration against cisplatin. (A) At 24 h after 100 ng/ml Dox induction, the LSD1-KD cells were exposed to 5 µg/ml cisplatin for additional 48 h, and cell apoptosis assay was performed using the Annexin V-FITC. (B) Expression levels of Bcl2 and Bax proteins were detected in the LSD1-KD cells via western blotting. (C) At 24 h following induction via 100 ng/ml Dox, the LSD1-OE cells were exposed to 5 µg/ml cisplatin for an additional 48 h, and a cell apoptosis assay was performed using Annexin V-FITC. (D) Expression levels of Bcl2 and Bax proteins were detected in the LSD1-OE cells via western blotting. (E) After 24 h of induction via 100 ng/ml Dox, the trypsinized LSD1-KD and (F) LSD1-OE cells were seeded in Transwell inserts and cultured with 5 µg/ml cisplatin in the presence of Dox for another 24 h, and then stained with crystal violet. (G) Following treatment with 100 ng/ml Dox for 24 h, the LSD1-KD and (H) LSD1-OE cells were cotreated with 5 µg/ml cisplatin for additional 24 h, after which the protein expression levels of epithelial-mesenchymal transition markers were detected via western blot analysis. Error bars represented data as the means ± standard error of the mean (n=3). *P<0.05, compared with the group not treated with cisplatin and Dox; #P<0.05, compared with the groups treated with cisplatin alone; &P<0.05, compared with the groups treated with Dox alone. Bcl2, B-cell lymphoma-2; Bax, Bcl2-associated X; FITC, fluorescein isothiocyanate; Snail, snail family transcriptional repressor 1.