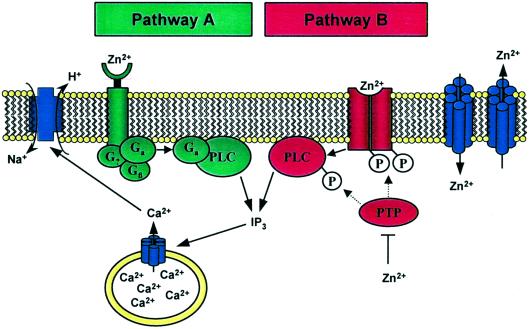
Figure 1.
The effect of extracellular zinc on cellular calcium signaling. (Pathway A), Mechanism proposed by Hershfinkel et al. (5). (Pathway B), Alternative pathway through control of protein tyrosine kinases and phosphatases by zinc. Both pathways lead to phospholipase C activation, mobilization of intracellular calcium, and activation of the Na+/H+ exchanger. Zinc exporters and importers control the transport of zinc between the extracellular space and the cytoplasm.