Figure 2. RB Promotes In Vivo Cellular Apoptosis in NSCLC.
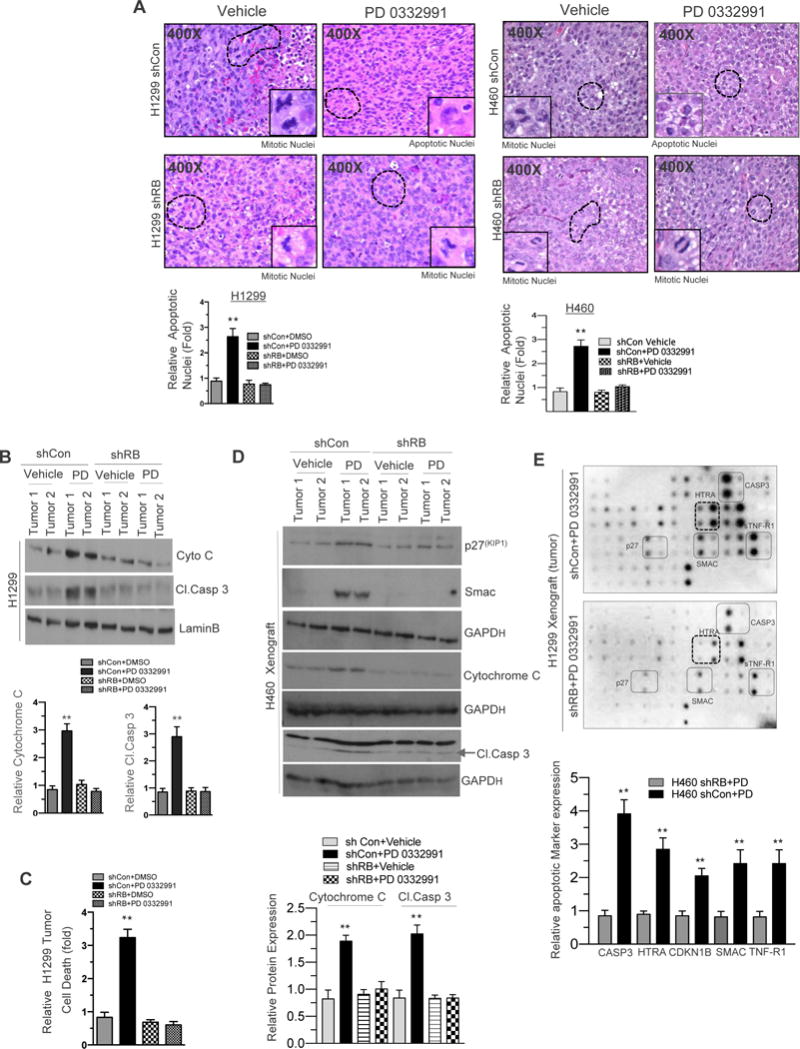
(A) H&E staining of shCon and shRB H1299 and H460 cell line induced xenografts (400×) in response to CDK4/6 inhibition (150 mg/kg body wt) and a graphic representation of apoptosis positive nuclei in RB proficient and deficient H1299 and H460 cell line induced xenografts in response to CDK4/6 inhibition (left and right panel). (B) Immunoblotting analysis of cytochrome C, Cleaved caspase3 and LaminB in shCon and shRB H1299 cell line induced xenografts in response to CDK4/6 inhibition (150 mg/kg body wt) and a graphic representation of cytochrome C and cleaved caspase 3 expression in shCon and shRB tumor lysates. (C) Graphic representation of cell death analysis via photometric enzyme immunoassay in shCon and shRB H1299 cells in response to CDK4/6 inhibition (150-mg/kg body wt). (D). Immunoblotting analysis of p27, Smac Cytochrome c, cleaved caspase 3 and GAPD in shCon and shRB H460 xenograft in response to CDK4/6 inhibitor (150 mg/kg body weight). (E) Apoptotic array (protein array) images from shCon and shRB H1299 cells induced xenografts in response CDK4/6 inhibition (150-mg/kg body wt) and a graphic representation of apoptotic markers and a graphic representation of Caspase3, HTRA, p27, Smac and TNFR-1 expression in shCon and shRB tumor lysates. In each group 5 or more animals were used and each data point is a mean ± SD from 5 or more animals or three or more independent experiments. **p <0.05 were considered as statistically significant.
