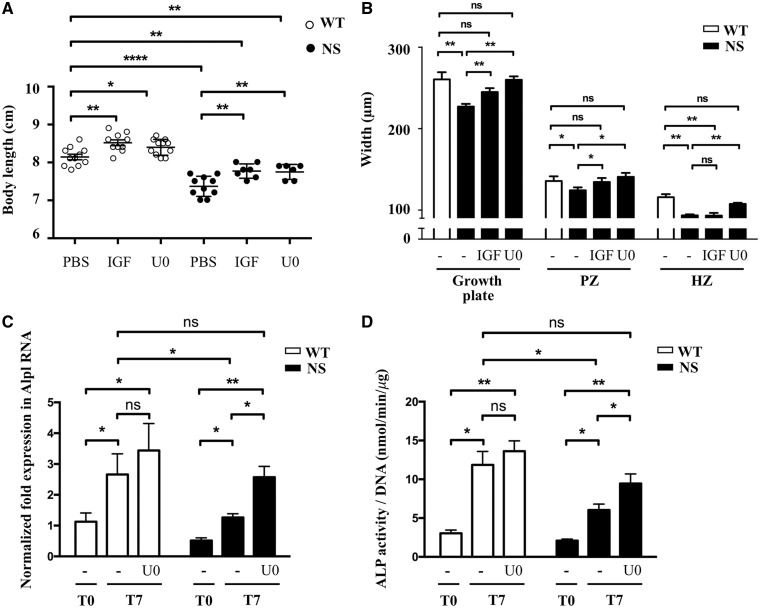
Figure 6.
RAS/ERK inhibition partially restores growth and growth plate abnormalities in NS mice. (A) Body length of 4-week-old WT and NS mice, treated i.p. from 1 to 4 weeks of age with vehicle (n WT/NS=11/10), IGF1 (4 mg/kg twice daily; n WT/NS=10/7) or U0126 (5 mg/kg daily; n WT/NS=11/6), are shown. IGF1 and U0126 treatments partially restored growth retardation in NS mice. (B) Measurement of growth plate zones widths after Alcian blue staining. IGF1 led to an increase of the length of the proliferating zone without correcting the hypertrophic zone shortening, while U0126 treatment restored the length of the growth plate, by simultaneously increasing the length of the proliferating and hypertrophic zones. (C and D) ALP expression determined by quantitative RT-PCR (C) and activity determined by fluorometric method using p-nitrophenol-phosphate used as a substrate (D), in WT (n=7) and NS (n=7) primary murine chondrocytes at baseline (T0) and after 7 days of differentiation with ascorbic acid, in the presence or absence of U0126 (10 μM) added to the culture medium. U0126 treatment restored ALP expression and activity in NS chondrocytes. Results of Alp expression are expressed as a fold change in mRNA expression compared with WT mice at baseline. ALP activity was normalized to the total DNA content of each sample. Values are means ± SEM. The statistical significance of fold changes was determined using a two-way repeated-measures ANOVA for comparison between T0 and T7 and a two-tailed Student’s t-test for comparison between WT and NS primary chondrocytes. Significant statistical differences between groups: ***P<0.001, **P<0.01, *P<0.05.