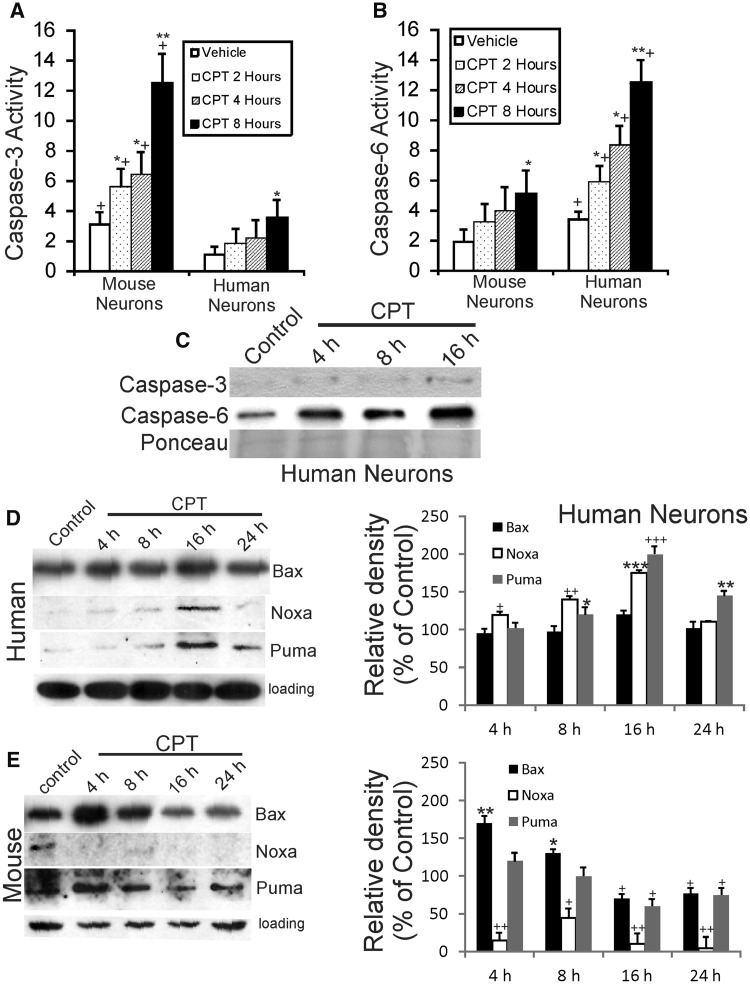
FIGURE 3.
Degenerating human neurons and mouse neurons use different caspases and use Bcl-2 family members temporally different. (A) Caspase-3 activity, determined by biochemical colorimetric assay, is increased abruptly and robustly in mouse forebrain neurons in a time-related manner after 10 µM CPT exposure. In contrast, human neurons have significantly less activation of caspase-3 activity compared to similarly cultured mouse neurons. Values (in units × 10−1) are mean ± SD (n = 3 different cultures). Significantly greater *p < 0.05, **p < 0.001 than control (same species comparison); +p < 0.01 and ++p < 0.001 (time-matched comparison of mouse neurons vs human neurons). (B) Caspase-6 activity, determined by biochemical colorimetric assay, is increased robustly in differentiated human forebrain neurons in a time-related manner after 10 µM CPT exposure. In contrast, mouse neurons have significantly less activation of caspase-6 activity compared to similarly cultured human neurons. Values (in units × 10−1) are mean ± SD (n = 3 different cultures). (C) Western blots for cleaved caspase-3 and cleaved caspase-6 in cell lysates of differentiated human neurons treated with DNA damaging agent (10 µM CPT). Degenerating human neurons display only a modest increase in cleaved caspase-3, while cleaved caspase-6 accumulates abruptly and robustly by 4–8 hours (h) and the accumulation progresses through 16 hours. Ponceau S-stained blot is shown to verify equivalent protein loading per lane. (D, E) Differentiated human neurons (D) and mouse neurons (E) were treated with vehicle or 10 µM CPT for 4, 8, 16, and 24 hours, and then total cell lysates were harvested for Western blotting for Bax, Noxa, and Puma. GAPDH Western blots show protein loading per lane. Graphs at right summarize Western blot densitometry results. Compared to vehicle-treated human neurons, CPT-treated human neurons showed significant increases in Bax at 16 hours (*p < 0.05), Noxa at 4, 8, and 16 hours (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, respectively), and Puma at 8, 16, and 24 hours (*p < 0.05, ***p< 0.001, **p < 0.01, respectively). Compared to vehicle-treated mouse neurons, CPT-treated mouse neurons showed significant increases in Bax at 4 and 8 hours (**p < 0.01, *p < 0.05, respectively) and significant decreases at 16 and 24 hours (+p < 0.05), significant decreases (+p < 0.05 or ++p < 0.01) in Noxa at 4, 8, 16, and 24 hours, and significant decreases (+p < 0.05) in Puma at 16 and 24 hours.