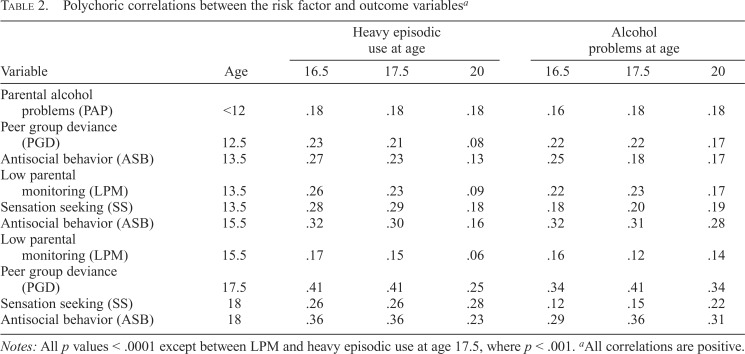
Table 2.
Polychoric correlations between the risk factor and outcome variablesa
| Variable | Heavy episodic use at age |
Alcohol problems at age |
|||||
| Age | 16.5 | 17.5 | 20 | 16.5 | 17.5 | 20 | |
| Parental alcohol problems (PAP) | <12 | .18 | .18 | .18 | .16 | .18 | .18 |
| Peer group deviance (PGD) | 12.5 | .23 | .21 | .08 | .22 | .22 | .17 |
| Antisocial behavior (ASB) | 13.5 | .27 | .23 | .13 | .25 | .18 | .17 |
| Low parental monitoring (LPM) | 13.5 | .26 | .23 | .09 | .22 | .23 | .17 |
| Sensation seeking (SS) | 13.5 | .28 | .29 | .18 | .18 | .20 | .19 |
| Antisocial behavior (ASB) | 15.5 | .32 | .30 | .16 | .32 | .31 | .28 |
| Low parental monitoring (LPM) | 15.5 | .17 | .15 | .06 | .16 | .12 | .14 |
| Peer group deviance (PGD) | 17.5 | .41 | .41 | .25 | .34 | .41 | .34 |
| Sensation seeking (SS) | 18 | .26 | .26 | .28 | .12 | .15 | .22 |
| Antisocial behavior (ASB) | 18 | .36 | .36 | .23 | .29 | .36 | .31 |
Notes: All p values < .0001 except between LPM and heavy episodic use at age 17.5, where p < .001.
All correlations are positive.