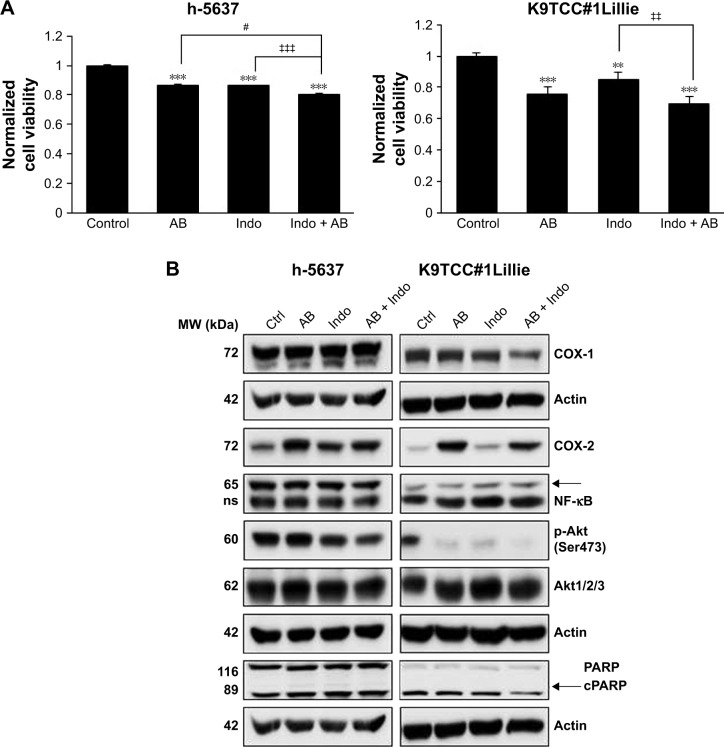
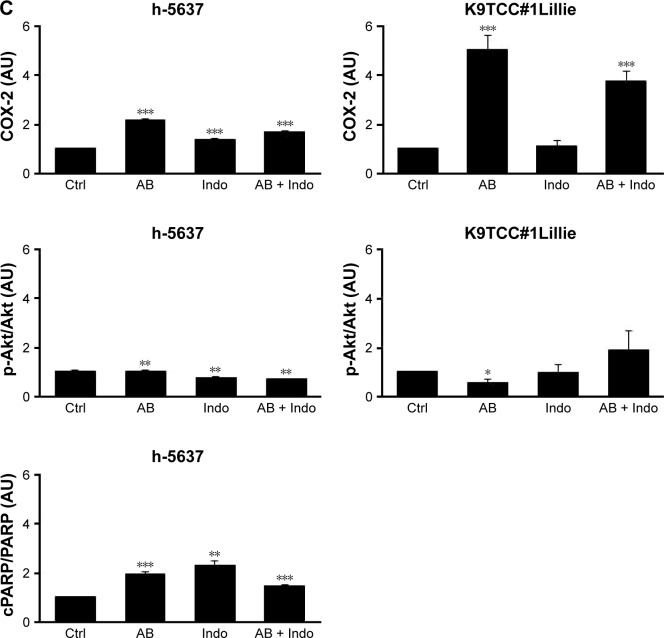
Figure 6.
Co-treatment of AB with Indo inhibited cell viability and AB-induced COX-2 expression in TCC cells. (A) h-5637 and K9TCC#1Lillie cells were treated with 5 μM AB, 50 μM Indo, and in combination (AB + Indo). Cell viability of TCC cells was determined by MTS assay. Co-treatment of AB with Indo inhibited cell viability more effectively than either treatment alone in bladder cancer cells. Values represent mean ± SE of four replicates of three independent experiments; paired Student’s t-test was used to compare the treatment to control groups, **p<0.01 and ***p<0.001. Student’s t-test was used to compare AB + Indo to AB treatment groups, #p<0.05. Student’s t-test was used to compare AB + Indo to Indo treatment groups, ‡‡p<0.01 and ‡‡‡p<0.001. (B) h-5637 and K9TCC#1Lillie cells were co-treated with 50 μM Indo and 5 μM AB, or each drug alone for 24 hours. The expression of COX-1, COX-2, NF-κB (specific band labeled with arrow), p-Akt (Ser473), Akt1/2/3, and cPARP (specific band labeled with arrow) proteins was determined by WB analysis. Actin was used as a loading control. AB-induced COX-2 expression was inhibited by co-treatment with Indo in h-5637 and K9TCC#1Lillie cells. (C) Densitometry analysis of COX-2, p-Akt (Ser473), and cPARP protein bands from WB analysis was performed using VisionWorks analysis software. Values represent the mean ± SE of the measured densitometry of each protein band of three independent experiments. Paired Student’s t-test was used to compare AB, Indo, and AB + Indo treatments to control groups, *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.
Abbreviations: AB, AB1010; Indo, indomethacin; COX, cyclooxygenase; WB, Western blot; TCC, transitional cell carcinoma; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhance of activated B cells; Akt, V-akt murine thymoma oncogene homolog 1; p-Akt, phosphorylated Akt; MTS, 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-5-(3-carboxymethoxyphenyl)-2-(4-sulfophenyl)-2H-tetrazolium salt; MW, molecular weight; cPARP, cleaved poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase; ns, non-specific.