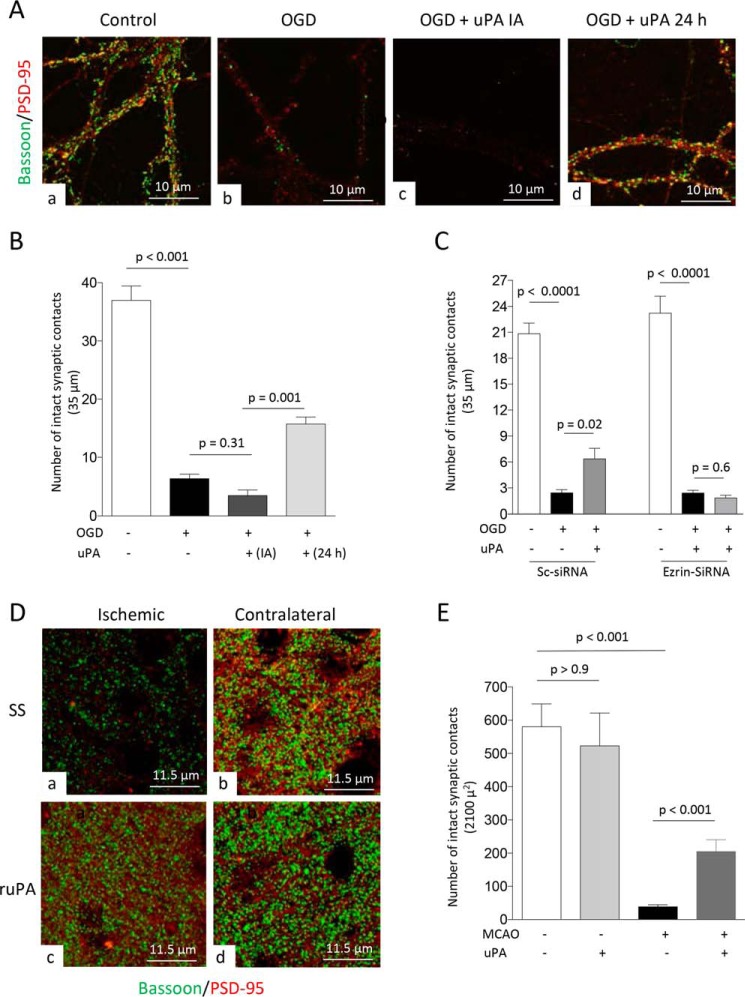
Figure 7.
uPA promotes ezrin-mediated synaptic recovery in the ischemic brain. A, representative confocal microscopy pictures at 40× magnification from dendrites from WT neurons maintained under normoxic conditions (panel a) or 24 h after 5 min of OGD and treatment with either PBS (panel b) or 5 nm of uPA either immediately after OGD (IA; panel c) or 24 h later (panel d). Green is bassoon, and red is PSD-95. B, mean number of synaptic contacts in WT neurons exposed to the experimental conditions described in A. n = 66–74 extensions examined per experimental group from neurons from three different cultures. The lines denote S.E. C, mean number of intact synaptic contacts in WT neurons treated with ezrin siRNA or Sc-siRNA and exposed to 5 min of OGD conditions. Twenty-four hours later, the cells were treated with 5 nm of uPA or as comparable volume of PBS. n = 40 neurons from three different cultures per experimental group. The lines denote S.E. D and E, representative confocal microscopy pictures at 60× magnification and electronically enlarged 4.6 times (D) from the ischemic area (panels a and c) and a comparable zone in the contralateral nonischemic hemisphere (panels b and d), and quantification of number of intact synaptic contacts in each area (E), in WT mice following 30 min of tMCAo and 24 h of recovery. The animals were intravenously treated with either SS or ruPA 24 h after tMCAo. Three hours later, the brains were harvested for the different observations. n = 14 cuts examined per animal from three different animals per experimental group. The lines in E denote S.E.