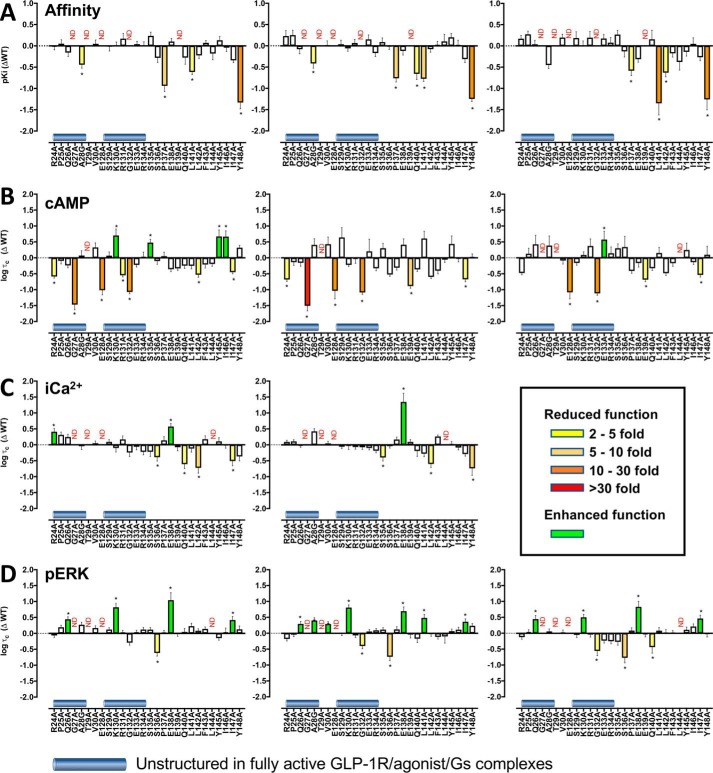
Figure 3.
Changes in affinity (A) and efficacy (B–D) of the agonists GLP-1, exendin-4, and oxyntomodulin at mutant GLP-1Rs. A, pKi values for the agonist peptides were derived from competition of 125I–exendin-4(9–39) binding. Data were plotted as differences in pIC50 of the alanine mutants compared with the wildtype (WT) hGLP-1R for GLP-1 (left panel), exendin-4 (middle panel), and oxyntomodulin (right panel). All pIC50 values were mean ± S.E. of three independent experiments performed in triplicate. B–D, Δlogτc values are the difference in the coupling efficacy (logτc) for cAMP accumulation (B), [Ca2+]i mobilization (C), and ERK phosphorylation (pERK) (D) of the alanine mutant GLP-1Rs compared with the WT receptor for GLP-1 (left panels), exendin-4 (middle panels), and oxyntomodulin (right panels). All functional values are mean ± S.E. of four to six independent experiments, conducted in duplicate. One-way ANOVA and Dunnett's post-test were performed to determined statistical differences (*, p < 0.05), and the bars are colored according to the fold-change between WT and mutant receptors (yellow, 2–5-fold decrease; light orange, 5–10-fold decrease; dark orange, 10–30-fold decrease; red, >30-fold decrease; green, increased affinity (A) or efficacy (B–D)). N.D., not defined.