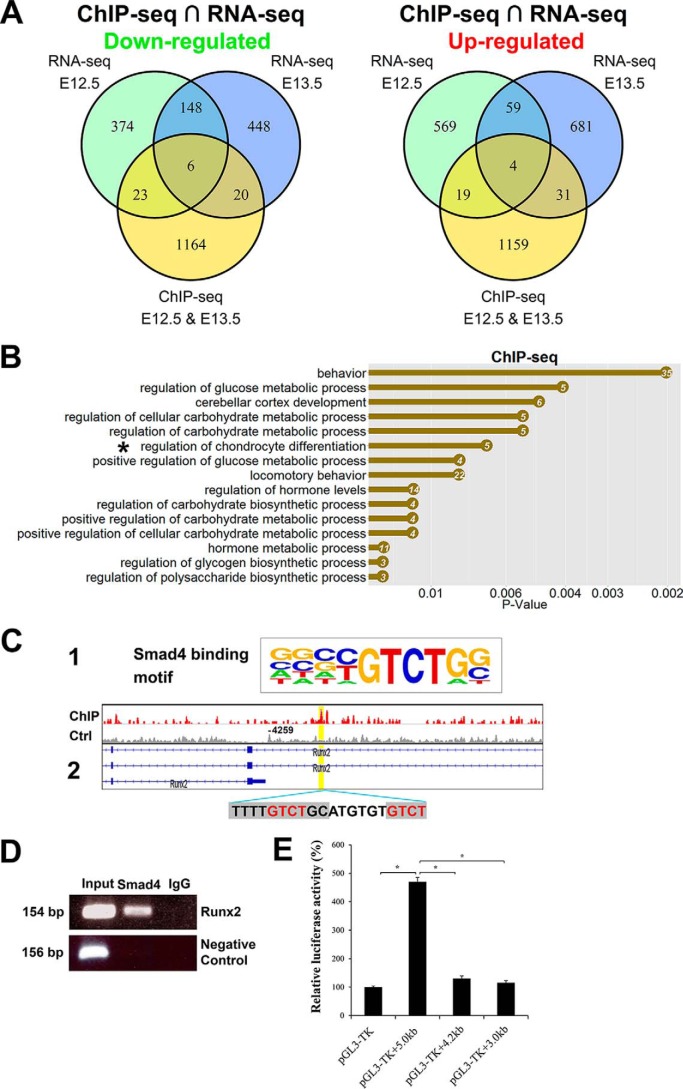
Figure 7.
Genomewide Smad4-binding sites are associated with chondrocyte differentiation. A, Venn diagrams show the number of down-regulated and up-regulated overlapping genes in E12.5 and E13.5 forelimbs analyzed by ChIP-seq and RNA-seq. B, top biological process GO terms were determined by DAVID in Smad4-binding genes. X axis is the p value for the enrichment of a GO term in the input gene list compared with genes in the whole genome. The number of genes is listed in the dots. C-1, Smad4-binding motif in the HOMER database. C-2, ChIP-seq analysis shows Smad4-binding site on the Runx2-regulatory region (binding motif was marked by gray and core sequence was labeled by red). D, ChIP-PCR verification of Smad4 binding on the Runx2-regulatory region. ChIP was performed anti-Smad4 antibody. A positive band was amplified using primers spanning the Smad4-binding site in the Runx2 promoter with input DNA (lane 1) and Smad4-ChIPed DNA (lane 2), but was not amplified with template ChIPed by IgG (lane 3). Negative control is PCR with GAPDH-CNAP1 primers. E, luciferase reporter assays of the Smad4 expression vector with various Runx2 promoter fragments. The putative Smad4-binding site is present in the 5.0-kb fragment, but not in the 3.0- and 4.2-kb fragments. *, p < 0.01.