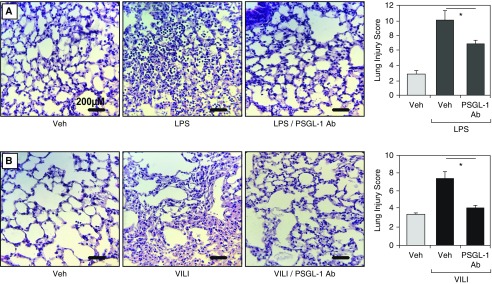
Figure 3.
Effects of a neutralizing PSGL-1 (P-selectin glycoprotein ligand 1) antibody on ventilator-induced lung injury (VILI) and LPS-induced histological indices of lung injury. (A) In vivo PSGL-1 inhibition with a neutralizing antibody (CD162, intravenous injection, 1 mg/kg) attenuates LPS-mediated lung injury. Compared with mice treated with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) vehicle (Veh), PSGL-1 antibody–pretreated mice exhibited fewer inflammatory cells, reduced alveolar wall thickness, and significantly lower histology injury scores. (B) In vivo PSGL-1 inhibition with CD162 also attenuates ventilator-mediated lung injury, with fewer inflammatory cells, reduced alveolar wall thickness, and significantly lower lung injury scores compared with PBS vehicle mice. Results are expressed as mean (±SEM); n = 3–5 per condition; *P < 0.01. Ab = antibody.