Figure 1.
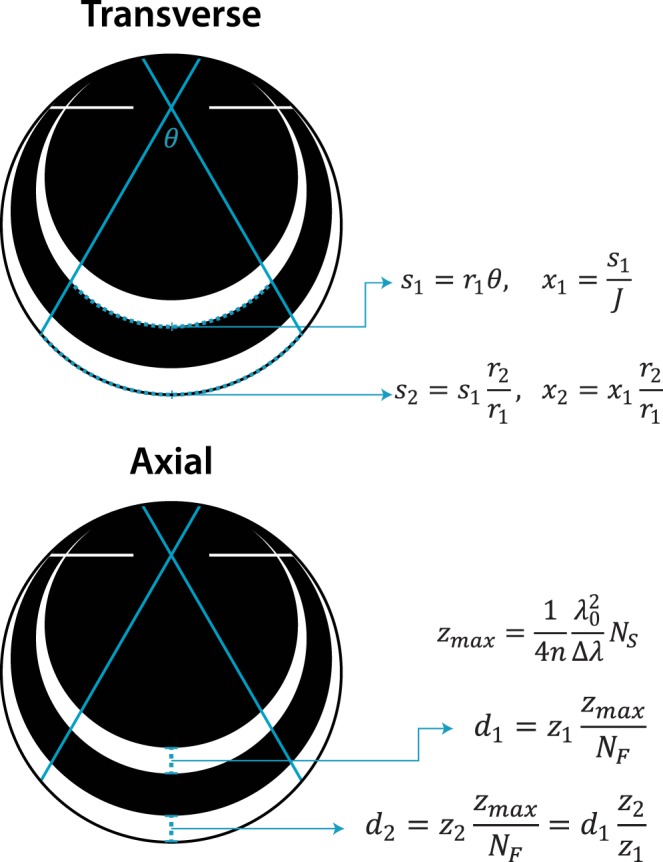
Ocular magnification affects transverse but not axial scaling. Arc length (s) of the imaged region is proportional to axial length (2r) for a given scan angle (θ). Dividing by J samples yields the transverse spatial scale (x). The maximum depth imaged (zmax) depends on the refractive index of the sample (n), center wavelength (λ0), bandwidth (Δλ), and spectrometer sampling (NS). Dividing zmax by the spectrometer sampling (NF) yields the axial spatial scale, which transforms a distance measurement (z) from pixels to linear space (d). Note that only transverse scale depends on axial length.
