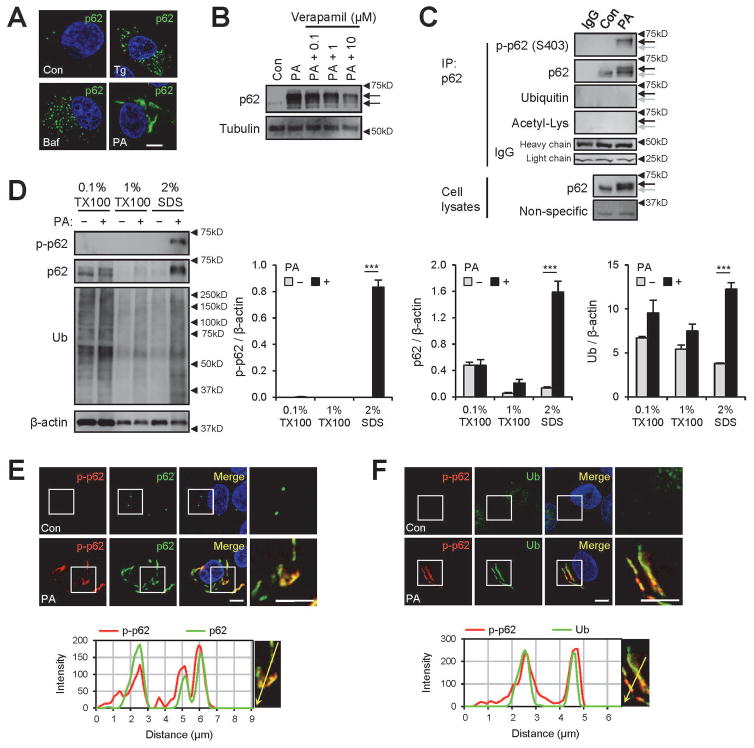
Fig. 1.
Saturated fatty acid (SFA)-induced lipotoxicity provokes p62/SQSTM1 phosphorylation in insoluble inclusion bodies. HepG2 cells were treated with BSA (Con), palmitic acid (PA, 500 μM), thapsigargin (Tg, 1μM), bafilomycin A1 (Baf, 100 nM) or PA + verapamil (0.1, 1, or 10 μM) for 9 h and subjected to the following analyses. (A,B) Cells were subjected to immunostaining (A) and immunoblotting (B). Arrows indicate band shifts of p62. (C) PA-untreated (Con) and -treated cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) using anti-p62 antibody or control IgG. IP complex and whole cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting. Background non-specific and IgG chain bands were identified from p62 and ubiquitin blots, respectively, and used as loading controls. Arrows indicate positions of shifted (black) and unshifted (grey) p62 bands. (D) Cells were subjected to serial protein extraction (solubility fractionation) with indicated concentration of Triton X-100 (TX100) or sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) and analyzed by immunoblotting with indicated antibodies (left panel) and quantified (right panels). (E,F) Cells were subjected to immunostaining with indicated antibodies (upper panels) and analyzed by line-scan evaluation of each signal across protein inclusions (lower panels). DNA was stained with DAPI (blue). Boxed areas in fluorescence images are magnified in right-most panels. Scale bars, 5 μm. Quantification data are shown as mean ± s.e.m. ***P < 0.001 (Student’s t-test). Arrowheads indicate the exact or nearest position of the protein molecular weight markers (kD).