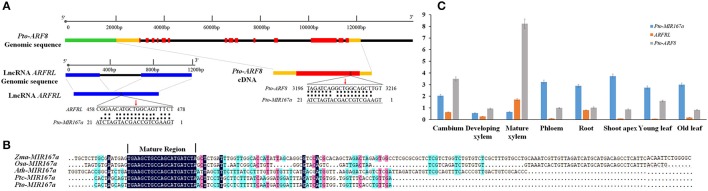
Figure 1.
Characterization and expression analysis of Pto-MIR167a and its targets, lncRNA ARFRL, and Pto-ARF8. (A) The structures of the Pto-ARF8 gene and long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) gene ARFRL, and the binding sites of Pto-miR167a with lncRNA ARFRL and Pto-ARF8. Green, orange, red, blue, and black lines represent the promoters, 5′/3′ untranslated regions (UTRs), exons, lncRNA transcripts, and introns/flanking regions, respectively. Red arrows represent the cleavage sites confirmed by 5′ rapid amplification of cDNA ends (5′-RACE). (B) Sequence alignment of the pre-miRNA region of the MIR167a genes of Zea mays (Zma), Oryza sativa (Osa), Arabidopsis thaliana (Ath), Populus trichocarpa (Ptc), and P. tomentosa (Pto). (C) The relative expression levels (arbitrary units normalized to the control) of Pto-MIR167a and its targets, lncRNA ARFRL, and Pto-ARF8, in eight tissues: cambium, developing xylem, mature xylem, phloem, root, shoot apex, young leaf, and old leaf, assessed by RT-qPCR with Actin as the internal control.