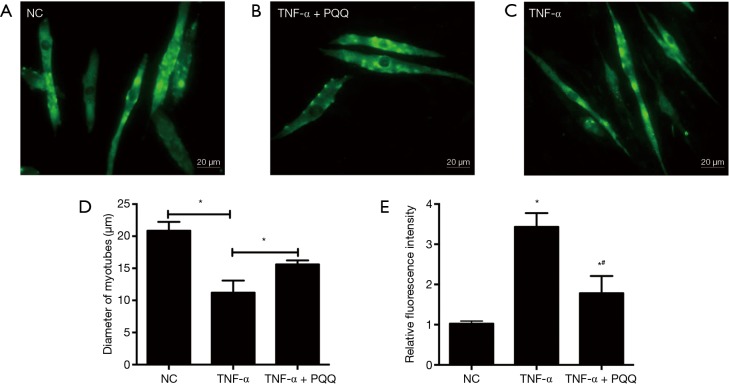
Figure 3.
PQQ treatments significantly avoided the reduction in the diameter of C2C12 myotubes induced by TNF-α through inhibiting ROS. (A-D) C2C12 myotubes were incubated with TNF-α for 24 h in the presence or absence of PQQ (80 µM). Then, immunodetection was performed to investigate the presence of MHC in C2C12 myotubes, and the value of the diameter of C2C12 myotubes was expressed as the mean ± SEM from three independent experiments; (E) PQQ could inhibit ROS caused by TNF-α treatment. DCF fluorescence intensities in C2C12 myotubes suffered from TNF-α treatment; NC: C2C12 myotubes without any treatment; TNF-α: C2C12 myotubes treated with TNF-α only; TNF-α + PQQ: C2C12 myotubes treated with TNF-α and PQQ simultaneously. *, P<0.05 versus NC; #, P<0.05 versus TNF-α. PQQ, pyrroloquinoline quinone; ROS, reactive oxygen species; DCF, dichlorofluorescein.