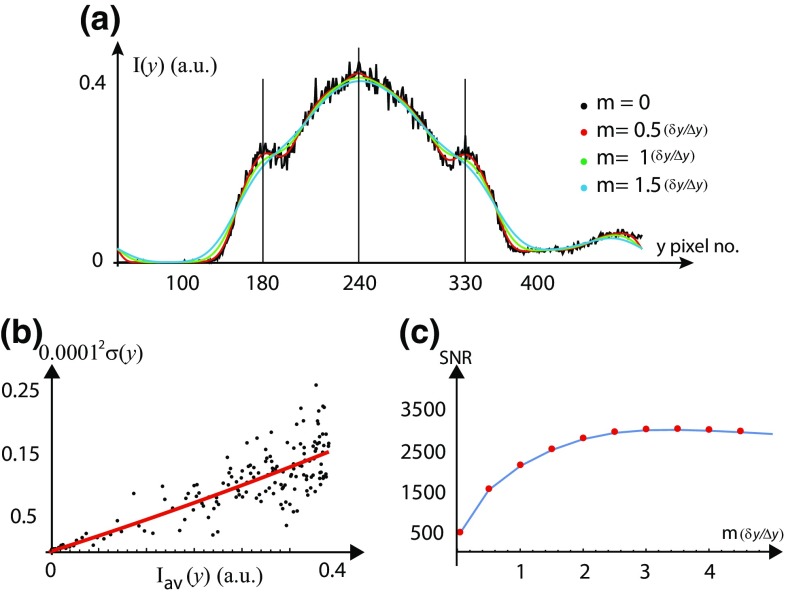
Fig. 4.
Improving the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of a feature in the image shown in Fig. 1b at cross section I. a Transverse 1-D fluorescence intensity profiles (arbitrary units, plotted against pixel number) are plotted on top of each other for (black), (0.5 (red), ( (green) and (1.5 (blue), for judging the smoothening operation. The PSF width in pixels is () for this image. The jump in the intensity profile beyond pixel no. is an artifact. b Plot of noise variance [] vs. average 1-D fluorescence intensity [(] of the tube. The red line shows a model fit to the data. c signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) is plotted as a function of the smoothening radius m in the units of . The peak signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of the feature is improved by six times from up to 3000 by smoothening operation