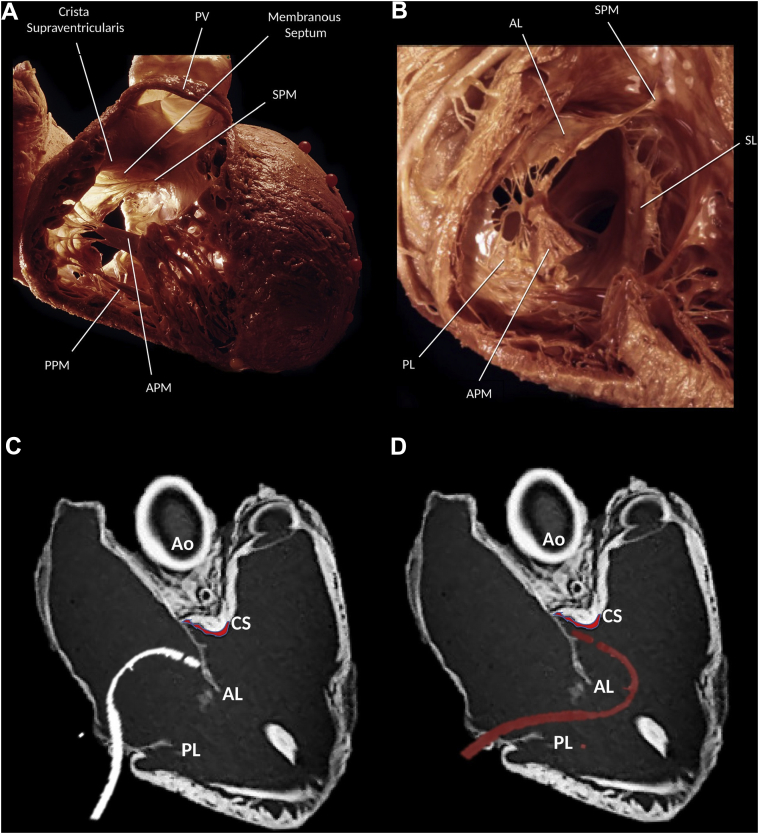
Figure 1.
A, B: Anatomy of the tricuspid valve (TV). (Reproduced from Dr K. Shivkumar with permission. Copyright UCLA Cardiac Arrhythmia Center, McAlpine Collection.) C, D: Computed tomography image of the heart showing the right ventricle inflow and outflow regions to demonstrate the position of the ablation catheter from a femoral approach. C: Ablation of tricuspid annular ventricular arrhythmias from an inferior approach limited by the ablation catheter being hindered by the anterior TV leaflet. D: Infratricuspid approach using a steerable sheath and a reversed S-curve allows to overcome this obstacle and reach the subvalvular tissue. AL = anterior leaflet; Ao = aorta; APM = anterior papillary muscle; CS = crista supraventricularis; PL = posterior leaflet; PPM = posterior papillary muscle; PV = pulmonic valve; SL = septal leaflet; SPM = septal papillary muscle.