Figure 6. Pre-exposure to a functional CD4 mimic alters the immunogenicity of unmutated, but not of interdomain-locked HIV-1 Env trimers.
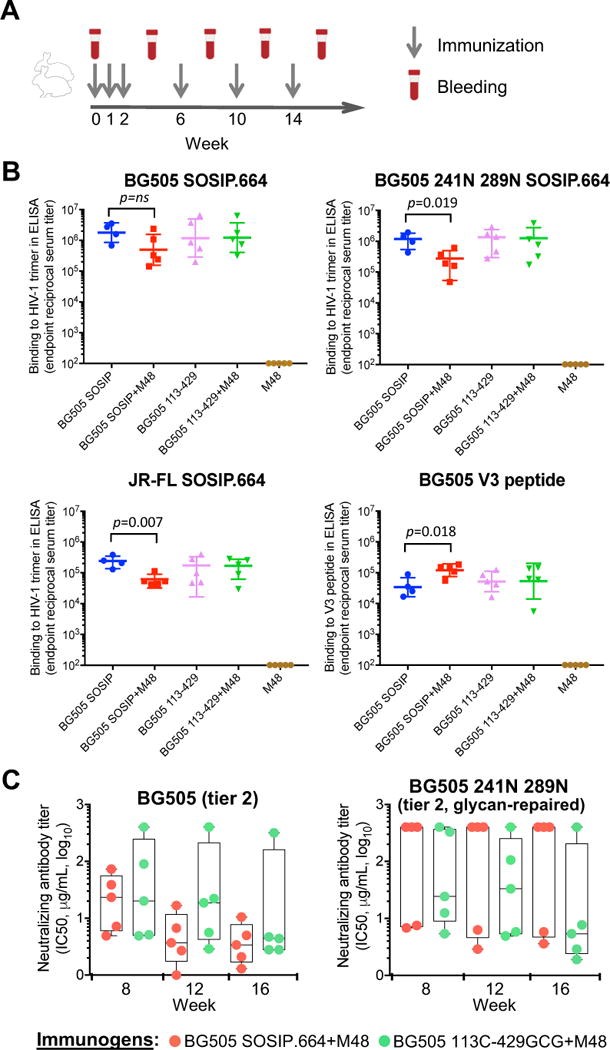
(A) Graphic scheme of the rabbit immunization protocol.
(B) Reactivity of immune rabbit sera with immobilized HIV-1 Env trimers or a V3 peptide, as tested by ELISA. Endpoint trimer- or peptide-binding titers are shown for week-16 sera obtained from rabbits immunized with unmutated or interdomain-locked HIV-1 BG505 SOSIP.664 trimers in the presence or absence of the CD4 mimic M48U1. Serially-diluted rabbit sera were tested on BG505 SOSIP.664, glycan-repaired BG505 (241N 289N) and JR-FL SOSIP.664 trimers, as well as on a BG505-derived linear V3 peptide. The data show endpoint titers for individual rabbits with geometric mean and standard deviation. P values were calculated using a two-tailed Mann-Whitney test using GraphPad Prism 7. Group 1 includes only 4 animals because one of them died from undetermined causes following the first immunization.
(C) Neutralization of HIV-1 pseudoviruses by purified serum IgG from rabbits immunized with unmutated or interdomain-stabilized HIV-1 BG505 SOSIP.664 trimers in the presence or absence of the CD4 mimic, M48U1. The data show half-maximal neutralizing IgG concentrations (IC50) for individual rabbits with means and minimum-to-maximum box and whiskers. Rabbit IgG were tested for neutralization of HIV-1 pseudoviruses bearing the wild-type BG505 Env (clade A, tier 2) or glycan-repaired BG505 Env (241N 289N, tier-2). Neutralization was assessed in TZM-bl cells. No statistical differences were found between the two groups of animals at any time point, as assessed using a two-tailed Mann-Whitney test. See also Tables S4 and S6.
