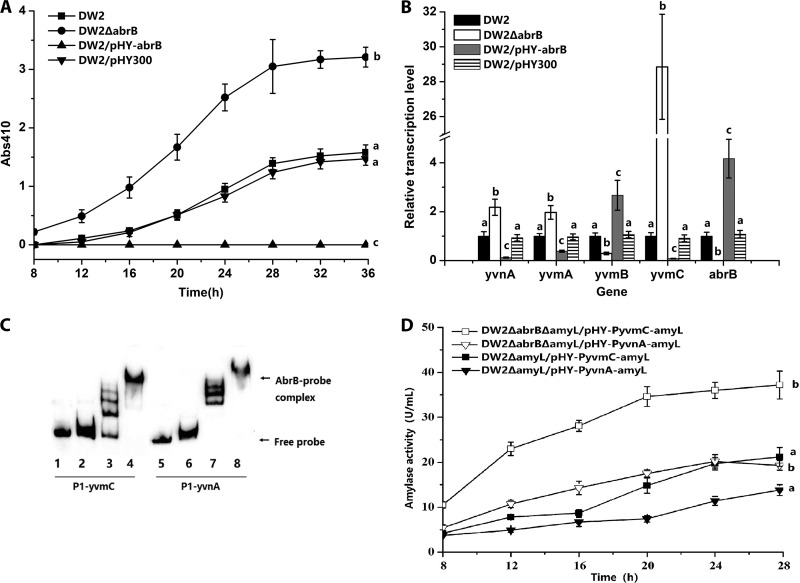
FIG 1.
AbrB negatively regulates pulcherriminic acid biosynthesis by binding to the promoter of yvmC-cypX. (A) Effects of abrB deletion (DW2 ΔabrB) and overexpression (DW2/pHY-abrB) on pulcherriminic acid production. (B) Gene transcription variations in abrB deletion and overexpression strains. The transcription levels of genes in DW2 were set to 1. (C) Binding of the AbrB protein to the promoter regions of yvmC and yvnA. Gel shifts of the labeled 91-bp P1-yvmC and P1-yvnA probes by the AbrB protein are shown. The concentrations of AbrB in lanes 1 to 8 were 0, 1, 2, 5, 0, 1, 2, and 5 ng/μl, respectively. Twenty nanograms of the P1-yvmC (lanes 1 to 4) or P1-yvnA (lanes 5 to 8) probe was added to each lane. The nonspecific competitor poly(dI-dC) was added to the EMSA binding buffer. (D) Expression-level comparisons of PyvmC-amyL and PyvnA-amyL transcriptional fusions. The amyL gene on the chromosome was deleted in DW2 and DW2 ΔabrB for the construction of DW2 ΔamyL and DW2 ΔabrB Δamy, respectively. pHY-PyvmC-amyL was then transformed into DW2 ΔamyL and DW2 ΔabrB ΔamyL to construct DW2 ΔamyL/pHY-PyvmC-amyL and DW2 ΔabrB ΔamyL/pHY-PyvmC-amyL. pHY-PyvnA-amyL was transformed into DW2 ΔamyL and DW2 ΔabrB ΔamyL to construct DW2 ΔamyL/pHY-PyvnA-amyL and DW2 ΔabrB ΔamyL/pHY-PyvnA-amyL.