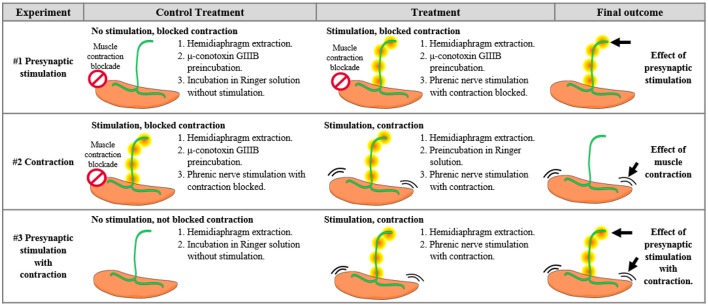
Table 1.
Differential effects of synaptic activity from those of muscle contraction.
“Synaptic activity includes the presynaptic events related with nerve stimulation (1 Hz, 30 min), synaptic transmission and endplate potential generation due to ACh signaling (referred to as the Stimulation condition in the figures). Muscle contraction includes membrane depolarization of the muscle fiber involving voltage-dependent sodium channels and the resulting myofiber contraction (referred to as the Contraction condition in the figures). Finally, presynaptic Stimulation with Contraction treatment comprises the effects of synaptic activity and muscle contraction, showing complete neuromuscular activity.”
The Table has been adapted from Table 1 in the original article “[Muscle Contraction Regulates BDNF/TrkB Signaling to Modulate Synaptic Function through Presynaptic cPKCα and cPKCβI] by [Erica Hurtado, Víctor Cilleros, Laura Nadal, Anna Simó, Teresa Obis, Neus Garcia, Manel Santafé, Marta Tomàs, Katherine Halievski, Cynthia Jordan, Maria Angel Lanuza, Josep Tomàs]” The original article is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited).