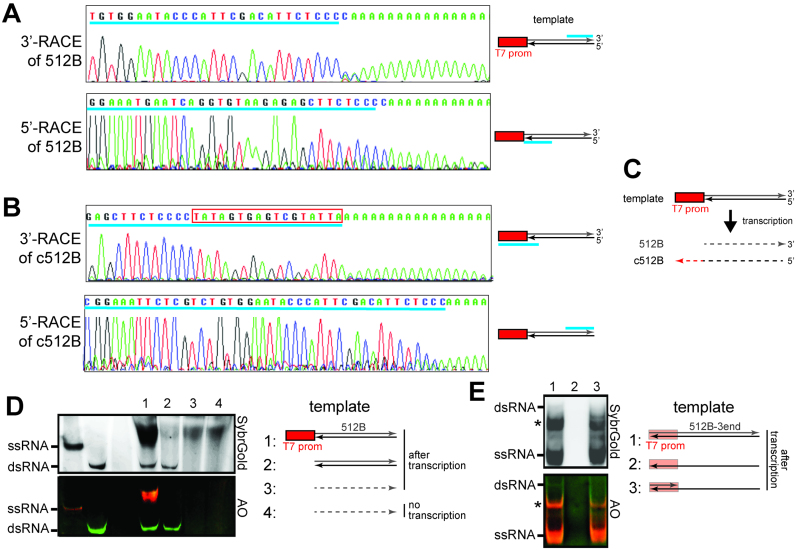
Figure 2.
The dsRNA byproduct is formed by sense and antisense RNAs generated in promoter-dependent and -independent manners, respectively. (A and B) Transcriptional start sites and end sites for the intended 512B product (A) and its complementary RNA byproduct (c512B) (B), as examined by 5′- and 3′-RACE. Transcriptional start and end sites are shown upstream of the poly A tail in the 5′- and 3′-RACE sequences, respectively. Cyan underscores in the sequence chromatograms indicate sequences matching those in the template. The location of the matching sequence in the template is shown in the schematic on the right. The red box in (B) indicates the reverse complement sequence of the T7 promoter. (C) Schematic illustrating the results in (A and B). Transcription using a template with a single T7 promoter results in the production of both sense and antisense transcripts, which differ in length by the size of the T7 promoter. Solid and dotted lines indicate DNA and RNA, respectively. (D) Native PAGE analysis of T7 transcripts generated using DNA template with a single T7 promoter (1), DNA template without the T7 promoter (2), and gel-purified 512B ssRNA as a template (3). RNA template alone (4) was compared with (3). (E) Native PAGE analysis of T7 transcripts generated using fully duplexed DNA template (1), template strand ssDNA alone (512B-3end in Supplementary Table S1) (2), and partially duplexed DNA template (generated by annealing 512B-3end with T7promoter_top_strand, Supplementary Table S1) (3). * indicates unknown ssRNA byproduct from transcription.