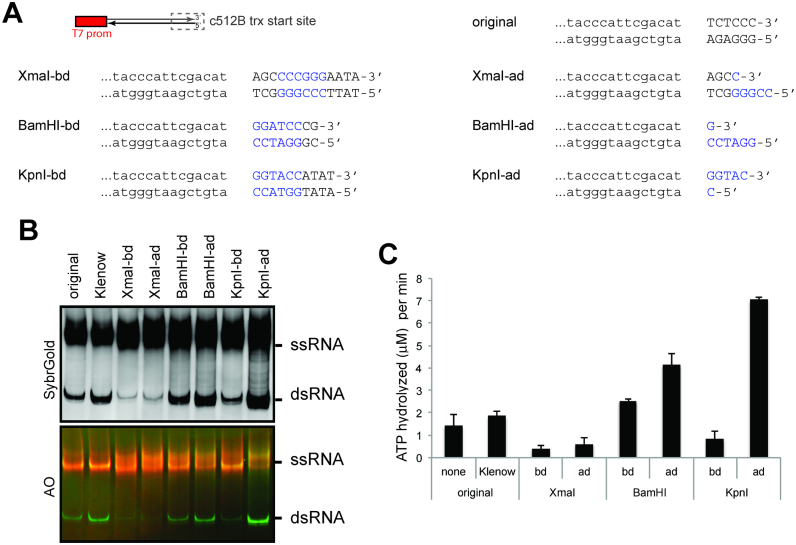
Figure 3.
Impact of the DNA termini sequence and structure on the promoter-independent antisense transcription. (A) Sequence and structure variants of DNA templates tested in this study. All have a single T7 promoter for transcription of 512B. The sequence near the promoter-less end (i.e. transcriptional start site for the antisense transcript, c512B) were varied and shown in capital letters. DNA end structural variants were generated by restriction digestion of the listed DNA. Restriction sites are colored blue, and –bd and –ad indicate before and after digestion, respectively. (B) Native PAGE analysis of the T7 transcripts produced using the original 512B template before and after the Klenow reaction, and its sequence variants before and after respective restriction digestions. (C). MDA5 ATPase assay of the T7 transcripts in (B) (mean ± S.D., n = 3 biological replicates).